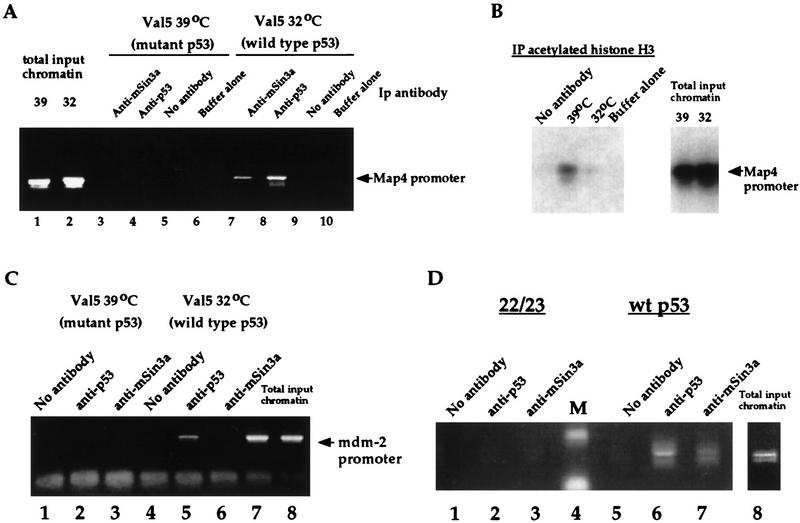
Figure 4.
Wild-type p53 and mSin3a interact with the Map4 promoter in vivo, resulting in decreased association of this promoter with acetylated histones. (A) ChIPs assay of the Map4 promoter (nucleotides −70 to +350, where +1 represents that start site of transcription) in Val5 cells cultured at 39°C (mutant p53) or 32°C (wild-type p53). IP of formaldehyde–cross-linked lysate was performed using 10 μg of anti-p53 or anti-mSin3a, followed by PCR using oligonucleotides specific for the Map4 promoter. As negative controls, lysis buffer alone was added to an anti-p53 IP (lanes 6,10), or lysate was incubated without antibody (lanes 5,9). The doublet band represents an occasional internal priming event seen with the Map4 reverse primer. For total input chromatin, 1 μl of a 1:300 dilution of DNA was used for the PCR. (B) ChIPs analysis of the Map4 promoter in Val5 cells using antisera specific for acetylated histone H3 (Upstate Biotechnology, Inc.). Following immunoprecipitation of Val5 extract and PCR of eluted chromatin, the agarose gel was blotted and hybridized to the full-length Map4 promoter. As negative controls, no antisera or 5 μg of anti-acetylated histone H3 was used for the IP of extract and binding buffer alone, respectively. (C) Wild-type p53, but not mutant p53 or mSin3a, associates with the mdm2 promoter in vivo. Immunoprecipitated chromatin from the experiment in A was used for PCR of the murine mdm2 promoter, using oligonucleotides that flank the p53-binding sites in this promoter. Prior to PCR for 25 cycles, immunoprecipitated chromatin was diluted 1:1000. For total input chromatin, 1 μl of a 1:300 dilution was used. (D) ChIPs assays were performed as above using extract from H1299 cells (human lung adenocarcinoma, p53 null) transfected with either human wild-type p53 (lanes 5–7) or human p53 containing mutations of amino acids 22 and 23 (lanes 1–3). Ten micrograms of polyclonal antisera to p53 or mSin3a (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), or no antibody, was used for immunoprecipitations, followed by PCR of the Map4 promoter. Western analysis indicated that equivalent levels of wild-type p53 and the 22/23 mutant were expressed in the transfected cells.