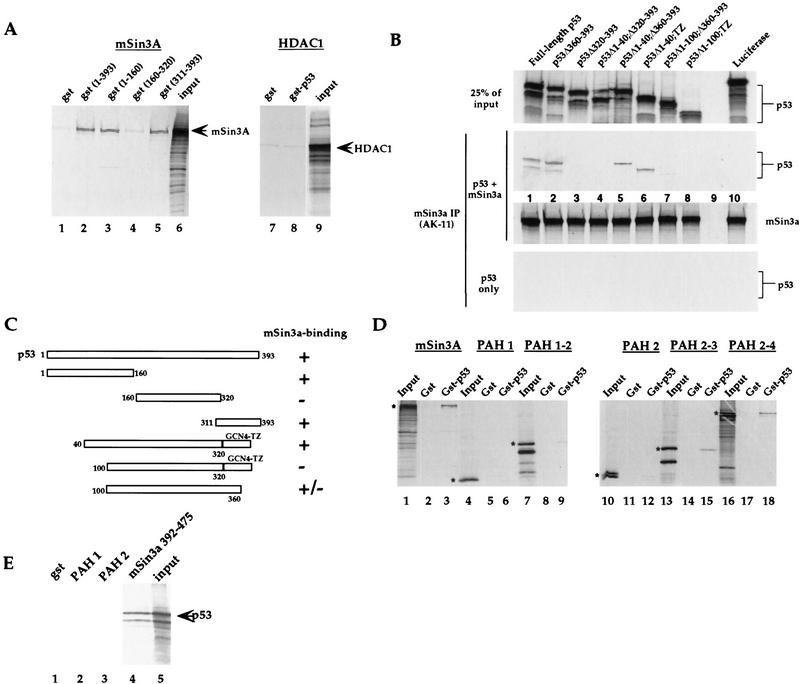
Figure 5.
p53 interacts with mSin3a in vitro. (A) GST fusion proteins of p53, which include the p53 amino acids listed, were assayed for binding to the in vitro-translated radiolabeled proteins listed above each panel. Input lanes include 50% of the radiolabeled input protein, unless noted otherwise. Arrows mark the major in vitro-translated product. These data indicate that p53 amino acids 1–160 (lane 3) and 311–393 (lane 5) interact with mSin3a in this assay. Negative controls include GST alone (lanes 1,7), and in vitro-translated HDAC1 (lanes 7,8). (B) Binding assays of in vitro-translated mSin3a (100% input in bottom panel) with in vitro-translated synthetic p53 mutants (25% of input in top panel). Although deletion of amino acids 360–393 of p53 does not inhibit interaction with mSin3a (middle panel, lane 2), deletion of amino acids 320–393 (the oligomerization domain, lane 3) abolished binding. Replacement of the p53 oligomerization domain with a modified leucine zipper tetramerization domain from GCN4 (TZ) allows for mSin3a binding (data not shown), and deletion of p53 amino acids 1–40 does not inhibit this binding (Δ1–40;TZ, lane 6). In contrast, deletion of amino acids 1–100 (Δ1–100;TZ) inhibits the ability of p53 to complex with mSin3a (middle panel, lane 8). As negative controls, luciferase showed undetectable binding to either mSin3a or p53, and mSin3a antiserum was unable to immunoprecipitate the p53 mutants incubated alone (bottom panel). (C) Summary of data obtained from in vitro binding assays; the combined data indicate that p53 amino acids 40–160 comprise the amino-terminal binding domain for mSin3a; amino acids 320–360 comprise the carboxy-terminal binding domain. (D) Binding of GST alone or a GST fusion protein encoding full-length p53 (GST–p53) with in vitro-translated radiolabeled full-length mSin3a, or mSin3a deletion mutants containing the paired amphipathic helical (PAH) domains listed above each panel. The mSin3a construct encoding PAH domains 2–3 constitutes the minimal p53 binding region. (E) A GST fusion protein containing mSin3a amino acids 392–475, which comprises the domain in between PAH domains 2 and 3, is sufficient to bind to in vitro-translated p53.