Table 3.
Iodination of phenol (1a) and 3,5-dichlorophenol (1b) using different iodination reagents.*
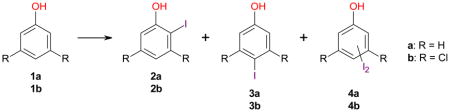 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Reaction Conditionsa | Reaction time (h) | Conversion (%) | Yield
|
||
| 2 (%) | 3 (%) | 4 (%) | ||||
| (A) Phenol (1a) | ||||||
| 3-1 | AgSbF6, I2, DCM | 23 | 79 | 2 | 1 | T |
| 3-2 | AgBF4, I2, DCM | 1.5 | 100 | 7 | 3 | T |
| 3–3 | AgPF6, I2, DCM | 23 | 91 | 4 | 46 | T |
| (B) 3,5-Dichlorophenol (1b) | ||||||
| 3–4 | Ag2SO4, I2, DCMb | 16 | 100 | 53 | 2 | T |
| 3–5 | AgSbF6, I2, DCM | 16 | <100 | 82 | T | nd |
| 3–6 | AgBF4, I2, DCMc | 1 | <100 | >90 | 5 | nd |
| 3–7 | AgPF6, I2, DCM | 16 | <100 | 57 | 10 | nd |
Percent conversion and yields were determined by GC-MS;
one equivalent (eq.) of each reagent was employed if not mentioned otherwise;
I2 (1.5 eq.) and Ag2SO4 (1.5 eq.);
I2 (1.1 eq.) and Ag2SO4 (1.1 eq.);
T = traces were detected by GC-MS; nd = not detected.
