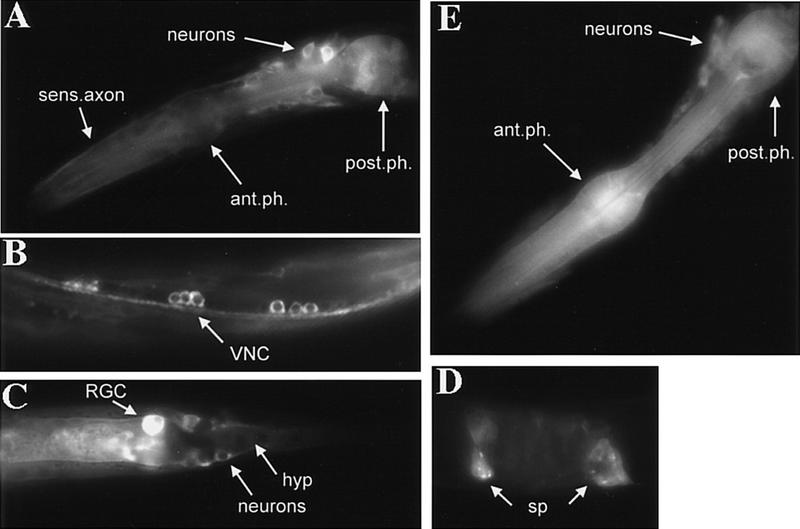
Figure 2.
AKT-1/GFP and AKT-2/GFP expression. (A–D) AKT-1/GFP expression; (E) AKT-2/GFP expression. (A) AKT-1/GFP expression in the head of an L2 animal. Expression in the anterior and posterior bulb of the pharynx (ant.ph. and post.ph.) is shown; expression in the isthmus of the pharynx is also observed. Many neurons in the head express AKT-1/GFP; expression in the neuronal nuclei is not visible. Also, expression can be seen in sensory axons (sens.axon) that proceed to the nose of the animal. (B) AKT-1/GFP expression in the ventral nerve cord (VNC) of an L1 animal (anterior is to the left). Both cell bodies (nuclei do not appear to express AKT-1/GFP) and axons of the VNC are clearly visible. Animal appears twisted because of coinjection with the rol-6 marker. (C) AKT-1/GFP expression in the tail of an L1 animal. The rectal gland cell (RGC), neurons of the tail with axons, and hypodermal cells (hyp) all clearly express AKT-1/GFP. AKT-1/GFP expression is not visible in the nuclei. (D) AKT-1/GFP expression in the spermatheca (sp) of an adult animal. (E) AKT-2/GFP expression in the head of an L4 animal. Expression in the anterior and posterior bulb of the pharynx (ant.ph. and post.ph.) is indicated; expression in the isthmus of the pharynx is also visible. Also shown is AKT-2/GFP expression in many neurons in the head; the nuclei appear to be excluded from AKT-2/GFP expression. AKT-2/GFP expression in the VNC, tail, and spermatheca was similar to that observed for AKT-1/GFP.