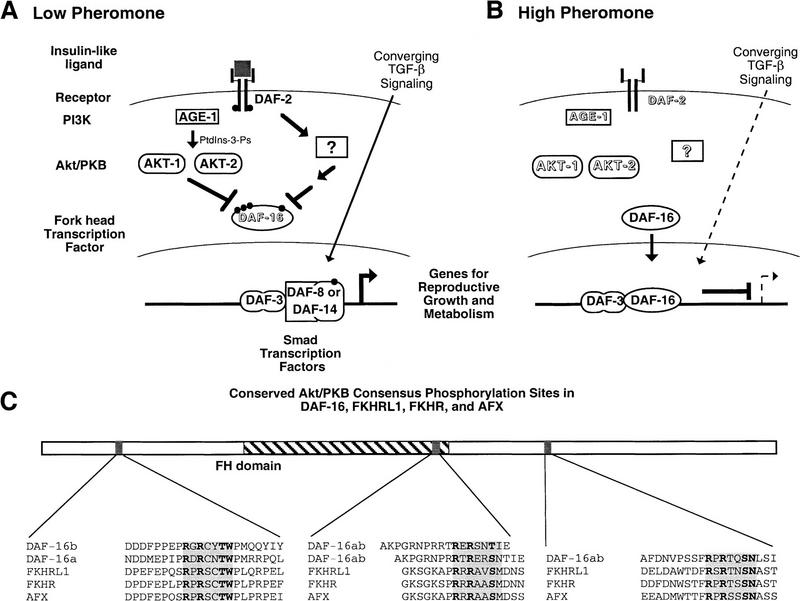
Figure 3.
Model for regulation of dauer formation by AGE-1 PI3K activation of AKT-1/AKT-2. (A) Normal growth occurs in conditions of low pheromone as a result of DAF-2 insulin receptor-like signaling and converging TGF-β signaling; DAF-16 is possibly inactivated by phosphorylation in these growth conditions. (See text for details.) (B) Dauer arrest occurs in conditions of high pheromone that cause lack of DAF-2 insulin receptor-like signaling and converging TGF-β signaling; DAF-16 may repress transcription in these conditions. (See text for details.) (C) Location and sequence context of consensus Akt/PKB phosphorylation sites in DAF-16 and the human homologs FKHRL1, FKHR, and AFX. daf-16 is differentially spliced to produce two gene products (DAF-16a and DAF-16b) that differ in the amino-terminal one-third of the protein but are identical (DAF-16ab) for the remainder of the protein. The consensus Akt/PKB phosphorylation site, RXRXXS/THyd (Alessi et al. 1996b), is boxed in gray and the amino acid residues identical in that site in all proteins are in boldface type.Other amino acid residues flanking these sites are also identical or show conservative substitutions in all proteins but are not in boldface type. The sites are located in the same relative regions of each protein, near the amino terminus, at the carboxy-terminal region of the Fork head DNA-binding domain (but downstream of the DNA recognition helix) and downstream of the Fork head domain. Note that two adjacent Akt/PKB consensus sites occur within the Fork head domain of DAF-16 and are shown aligned with a single Akt/PKB consensus site in FKHRL1, etc.