Figure 1.
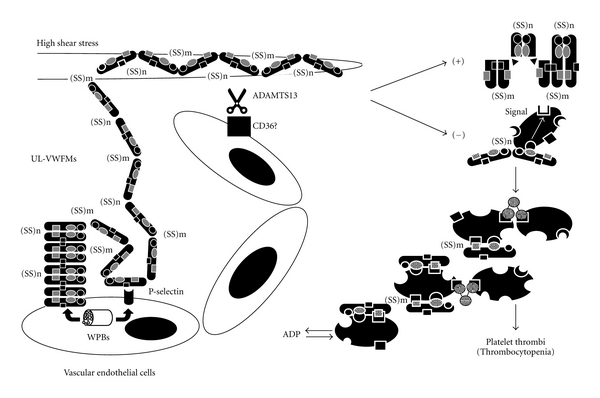
Proposed mechanism of platelet thrombi under high shear stress in the absence of ADAMTS13 : AC. Unusually large von Willebrand factor multimers (UL-VWFMs) are produced in vascular endothelial cells (ECs) and stored in Weidel-palade bodies (WPBs). UL-VWFMs are released from WPBs into the circulation upon stimulation by cytokines, hypoxia, DDAVP, and epinephrine. P-selectin that comigrates from WPBs anchors UL-VWFMs on the vascular EC surface. Under these circumstances, high shear stress changed the molecular conformation of UL-VWFMs from a globular to an extended form, allowing ADAMTS13 to access this molecule. In the absence of ADAMTS13 : AC, UL-VWFMs remain uncleaved, allowing them to excessively interact with platelet glycoprotein (GP)Ibα and activate platelets via intraplatelet signaling, which result in the formation of platelet thrombi. (Partially modified from Fujimura et al., [49]).
