Fig. 3.
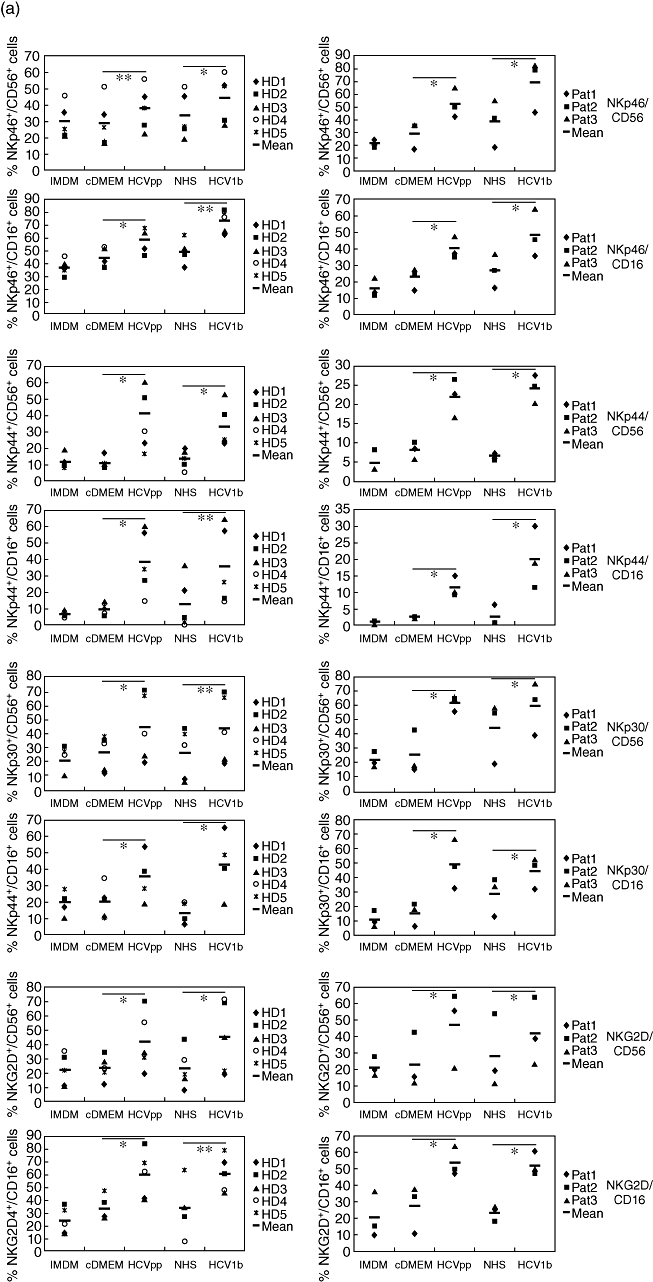
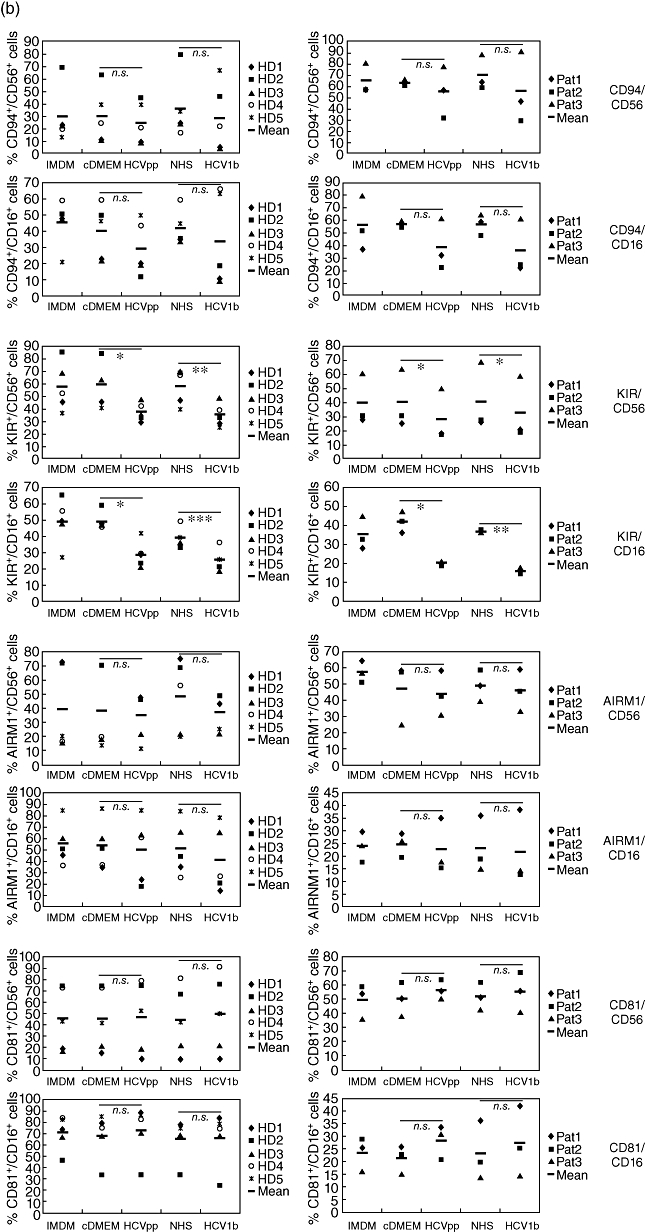
Increased expression of activating receptors and decreased expression of inhibitory receptors on natural killer (NK) cells after exposure to hepatitis C virus (HCV). NK cells from five healthy donors (HD, panels on left side) and three chronic HCV patients (Pat., panels on right side) were cultured for 5 days in either NK cell medium [Iscove's modified Dulbecco's medium (IMDM)] with interleukin-2/phytohaemagglutinin-P (IL-2/PHA-P)/feeders alone, or supplemented (1:1) with Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) conditioned by untransfected HEK293T cells (cDMEM), HCV pseudoparticles (HCVpp)-containing supernatant from transfected HEK293T cells, normal human serum (NHS) or human serum containing HCV1b, as indicated. Cells were analysed by multi-colour flow cytometry. (a) Frequencies of cells stained for either CD56 or CD16, and for one of the activating receptors NKG2D, NKp46, NKp44 or NKp30 are indicated. (b) Frequencies of cells stained for CD56 or CD16, and for one of the inhibitory receptors CD94/KLRD1 or AIRM1/p75, the KIR/CD158 receptor family, or for the cellular HCV-E2 ligand CD81/TAPA1 are indicated. The mean values of NK cell frequencies are shown. The differences between the cDMEM- and HCVpp-, as well as between the NHS- and HCV1b serum-treated groups, were evaluated by a paired two-tailed Student's t-test; n.s.: not significant; *P < 0·05; **P < 0·01; ***P < 0·001.
