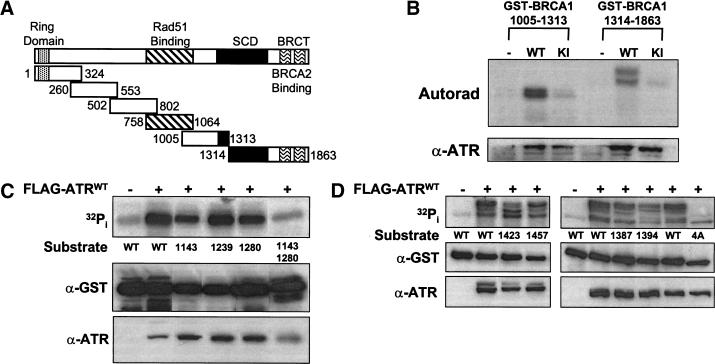
Figure 2.
ATR phosphorylates BRCA1 in vitro. (A) Schematic depiction of the six GST–BRCA1 fusion proteins tested as ATR substrates in immune complex kinase assays. SCD designates the S-Q cluster domain. (B) Phosphorylation of GST–BRCA1 fusion proteins requires a functional ATR kinase domain. HEK 293T cells were transiently transfected with either pcDNA3 (−), or plasmid constructs encoding FLAG-tagged wild-type ATR (WT), or FLAG-tagged catalytically-inactive ATR (KI). Cellular extracts were immunoprecipitated with α-FLAG mAb, and immune complex kinase assays were performed with GST–BRCA1 (1005–1313) or GST–BRCA1 (1314–1863) as the substrates. The levels of phosphorylated fusion protein and FLAG–ATR expression are presented at top and bottom, respectively. The other four GST–BRCA1 substrates depicted in A, were not phosphorylated by ATR above background levels (not shown). (C) Identification of ATR phosphorylation sites in GST–BRCA1 (1005–1313). ATR immune complex kinase assays were performed using cell lysates prepared from HEK 293T cells that had been transfected with either pcDNA3 (−) or FLAG–ATRWT (+). Wild-type (WT) or mutant GST–BRCA1 (1005–1313) fusion proteins containing either single or combination Ala substitutions at the indicated residues were used as substrates. (D) Identification of ATR phosphorylation sites in GST–BRCA1 (1314–1863). Wild-type (WT) or mutant GST–BRCA1 (1314–1863) fusion proteins containing single Ala substitutions at the indicated residues, or a GST–BRCA1 (1314–1863) mutant protein (4A) containing Ala substitutions at Ser 1387, Thr 1394, Ser 1423, and Ser 1457, were used as substrates in ATR kinase assays. Each panel represents a single experiment that is representative of the results obtained in independent trials.