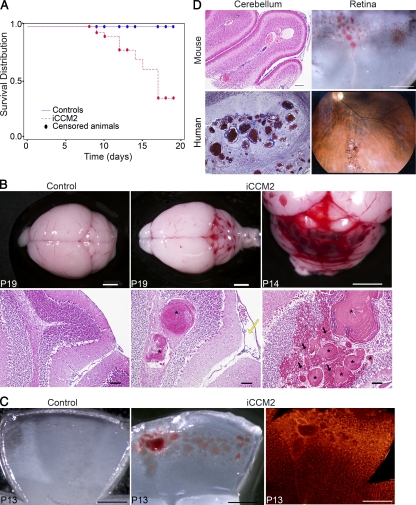
Figure 1.
Endothelial Ccm2 deletion at P1 results in CCM malformations mimicking the human CCM lesions in the cerebellum and in the retina. All animals were injected at P1 with 10 µl tamoxifen (equivalent to 20 µg) and dissected at the indicated time. Genotypes of inducible CCM2 KO (iCCM2) and control animals were respectively Cdh5(PAC)-CreERT2; Ccm2Del/fl and Cdh5(PAC)-CreERT2; Ccm2+/fl. (A) Kaplan-Meier survival curve from the control group (blue line, n = 110) and the iCCM2 group (dotted red line, n = 56). Circles represent censored animals, which were sacrificed for analysis. (B) Control and iCCM2 mouse brains upon dissection (top) and after H&E staining (bottom; n = 6 in each group from 4 different litters, analyzed between P11 and P19). CCM malformations, located in the cerebellum of iCCM2 animals, are composed by single or multiple caverns (asterisks) with extensive hemorrhage (black arrows) around the juxtaposed vascular cavities. Note the dilation of meningeal vessels in the iCCM2 (yellow arrow). (C) Control and iCCM2 mouse retinas at P13 upon dissection (left and middle) and after isolectin-B4 staining (right, n = 7 in each group from 4 different litters, analyzed between P11 and P15). (D) Mouse lesions phenocopy human CCM lesions. (left) Histology of the cerebral lesions in mouse and human. (right) Mouse retina upon dissection and human retinal angiography Bars: 2 mm (B, top); 500 µm (C and D, mouse retina); 100 µm (B [bottom] and D [mouse cerebellum]).