Figure 1.
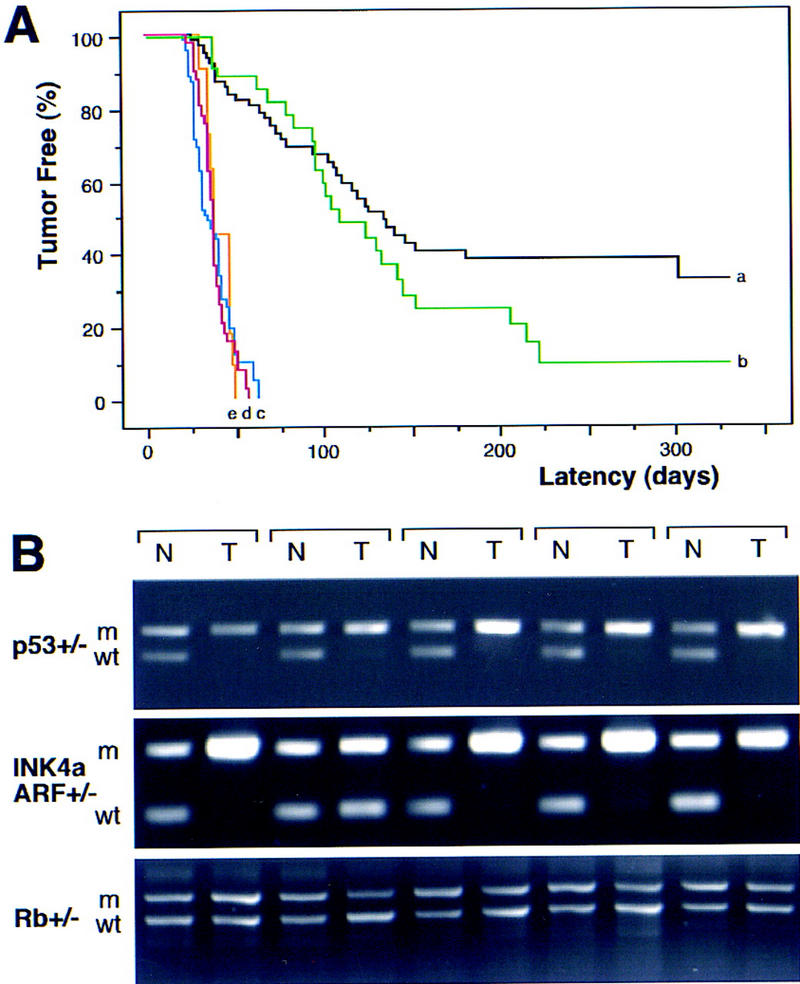
Tumor development in Eμ–myc transgenic mice. (A) Lymphoma incidence in Eμ–myc transgenic mice in the wild-type (control) background (n = 65; black, a) and in mice heterozygous for Rb (n = 39; green, b), INK4a/ARF (n = 41; blue, c), p53 (n = 73; red, d), and INK4a/ARF; p53 double heterozygotes (n = 11; orange, e). By day 70, all p53+/− and INK4a/ARF+/− mice developed lymphoma, whereas >75% of Rb+/− and control mice remained tumor free. (B) Matched normal (N) and tumor (T) DNA were isolated from tail and lymph nodes and analyzed by allele-specific PCR for the targeted gene [(m) mutated allele; (wt) wild-type allele]. Shown are results from five Eμ–myc transgenic mice in each genetic background. Note that tumors arising in the INK4a/ARF+/−; p53+/− double heterozygotes invariably lost the wild-type p53 allele but never the INK4a/ARF allele.
