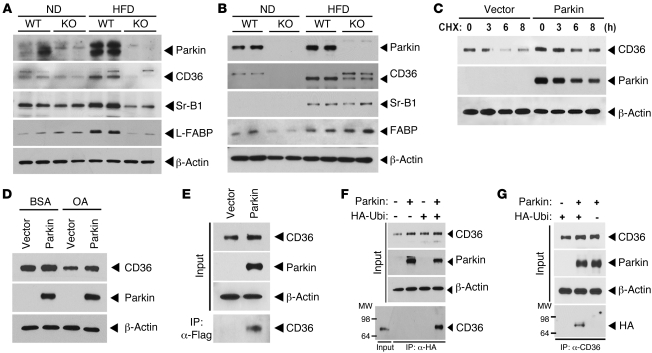
Figure 5. Parkin regulates posttranslational modification of CD36.
(A) Expression levels of Parkin and lipid uptake (CD36 and Sr-B1) and transport (L-FABP) proteins in response to the ND and HFD in liver tissue by immunoblot analysis. (B) Protein expression of Parkin and lipid uptake and transport proteins in response to the ND and HFD in whole brain tissue by immunoblot analysis. (C) Degradation of CD36 protein following CHX administration in the presence or absence of Parkin overexpression in HeLa cells engineered to overexpress CD36. (D) CD36 protein expression in response to oleic acid administration following overexpression of Parkin or control vector. (E) Interaction between Parkin and CD36. CD36-overexpressing HeLa cells were transfected with p3×Flag vector or p3×Flag-Parkin, respectively. After 48 hours transfection, protein extracts were IP with anti-Flag M2 agarose (IP:α-Flag). (F) Ubiquitination of CD36 following IP of an HA antibody and immunoblot analysis for CD36. CD36-overexpressing HeLa cells were transfected with HA-Ubiquitin and/or Parkin. (G) Ubiquitination of CD36 following IP with a CD36 antibody and immunoblot analysis for HA following the transfection of HA-Ubiquitin and/or Parkin in the CD36-overexpressing HeLa cells. All studies were performed in duplicate, and at least 3 independent experiments were performed.