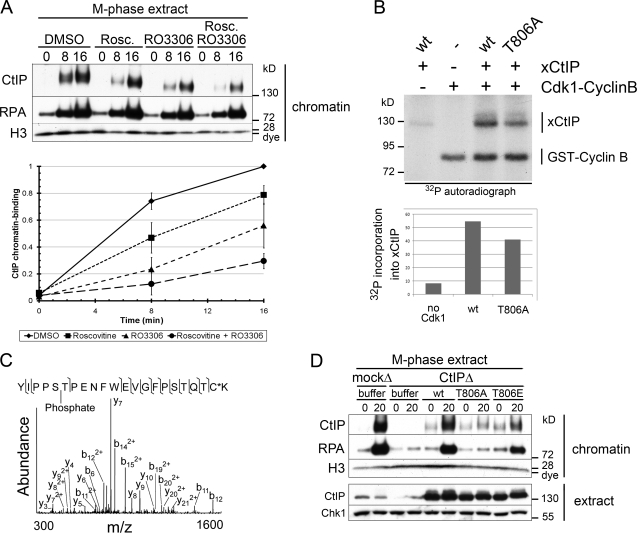
Figure 5.
Phosphorylation of CtIP by Cdk1 is required for M-phase resection. (A) Cdk activity is required for CtIP function and M-phase resection. M-phase extract was treated with DMSO, 200 µM roscovitine (Rosc.), 200 µM RO-3306, or both, and chromatin was isolated at the indicated time points (minutes) after addition of PflMI restriction endonuclease. Quantification of relative CtIP chromatin binding from three independent experiments is shown on the bottom, with error bars representing one standard deviation. (B) Cdk1–cyclin B kinase phosphorylates recombinant xCtIP in vitro. Recombinant Cdk1–cyclin B was incubated with recombinant xCtIP (wt or T806A) as indicated in the presence of γ-[32P]ATP. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. Quantification of the autoradiograph signal for xCtIP in this experiment is graphed on the bottom. Note that xCtIP-T806A incorporation is reduced by ∼25% because of the presence of multiple Cdk phosphorylation sites. (C) Tandem mass spectrometry of endogenous M-phase CtIP reveals phosphorylation at S805/T806. Tandem mass spectrum of phosphopeptide spanning residues 801–822. The experimental molecular mass of the intact precursor ion (2664.1613 D) closely matches the theoretical mass of the tryptic peptide 801–822 plus a phosphate group (2664.1607 D; mass difference = 0.0006 D). The fragmentation pattern confirms the identity of this phosphopeptide and narrows the localization of the phosphate group to either S805 or T806. The asterisk indicates that the cysteine residue was alkylated using iodoacetamide. (D) Conserved residue T806 is required for CtIP activity and resection in M phase. M-phase extract was mock depleted or CtIP depleted. CtIP-depleted extract was supplemented with buffer (−), wt xCtIP (wt), xCtIP-T806A (T806A), or xCtIP-T806E (T806E). PflMI restriction endonuclease (+) or buffer (−) was added, and chromatin was isolated after 15 min. Time points above are in minutes. m/z, mass to charge ratio.