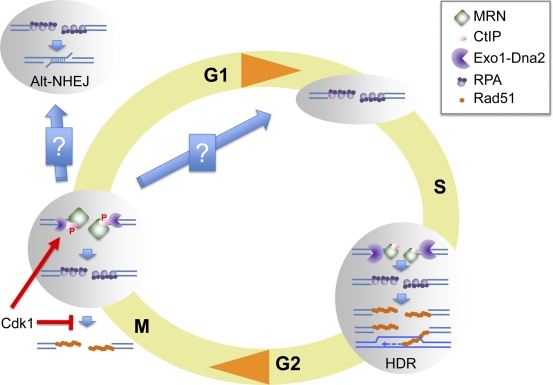
Figure 7.
Chromosomal DNA DSB resection in M phase. DNA DSBs generated in S phase are resected via the concerted action of MRN-CtIP and two additional pathways represented here as a single Exo1-DNA2 entity. S-phase resection generates ssDNA-RPA, which is competent for Rad51 filament assembly, a necessary step for HR. In contrast, DSBs generated in M phase are processed into ssDNA-RPA intermediates that do not support Rad51 chromatin assembly. Cdk1 promotes resection by phosphorylating CtIP while at the same time inhibiting Rad51 chromatin assembly. Resection initiation is dependent on MRN-CtIP in M phase as reflected by the relative size of the resection machinery components. M-phase resection generates ends that are not compatible for repair by NHEJ or by HR. These ends could be substrates for microhomology-mediated end joining in M or G1 phase. Alternatively, they could be transmitted to the next S phase and repaired by HR. P, phosphorylation.