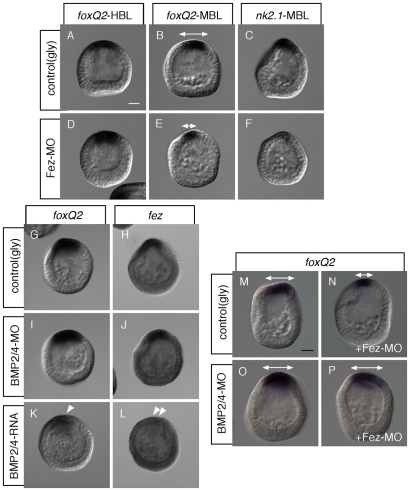
Fig. 4.
Fez attenuates BMP signaling, which antagonizes neurogenic ectoderm development. (A-F) Fez is required to maintain the size of the region expressing foxQ2 and nk2.1. (A) foxQ2 mRNA expression in control hatching blastula (HBL). (B) foxQ2 mRNA expression in control mesenchyme blastula (MBL). (C) nk2.1 mRNA expression in control MBL. (D) foxQ2 mRNA expression in Fez morphant HBL. (E) foxQ2 mRNA expression in Fez morphant MBL. (F) nk2.1 mRNA expression in Fez morphant MBL. (G-J) BMP2/4 does not suppress foxQ2 or fez expression outside the animal plate of MBL. (G) foxQ2 mRNA expression in control. (H) fez mRNA expression in control. (I) foxQ2 mRNA expression in BMP2/4 morphant. (J) fez mRNA expression in BMP2/4 morphant. (K,L) Mis-expressed BMP2/4 can suppress foxQ2 (K) and fez (L) expression. Single and double arrowheads show that in embryos over-expressing BMP2/4, both foxQ2 and fez expression is strongly reduced. (M-P) The foxQ2 expression domain is reduced in Fez morphants (N) versus controls (M), but not in double Fez/BMP2/4 morphant MBL (P) versus BMP2/4 morphant MBL (O). Double-headed arrows in B, E and M-P show foxQ2-positive animal plate. Scale bars: in A, 20 γm for A-F,I-N; in O, 20 γm for O-R.