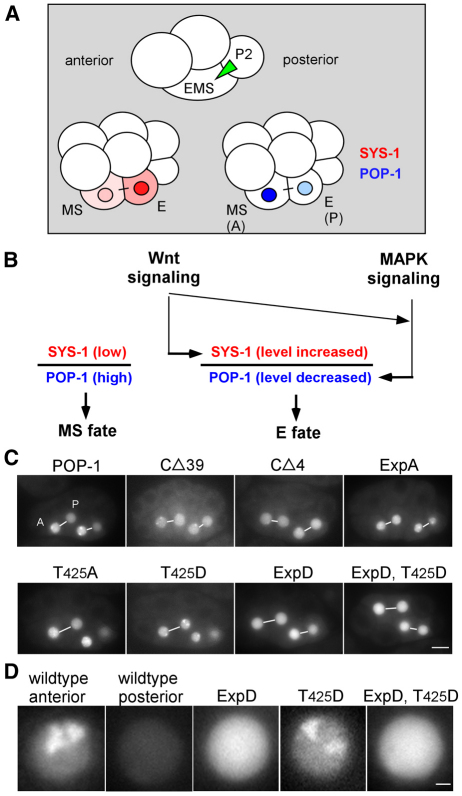
Fig. 1.
The POP-1 C-terminal domain is required for nuclear A-P symmetry. (A) Cartoon drawings of four-cell and eight-cell embryos, highlighting the P2-to-EMS signal (green triangle), and localization in MS and E blastomeres of SYS-1 (red) and POP-1 (blue). (B) Wnt and MAPK signal regulation of SYS-1 and POP-1 levels in MS and E. (C) Fluorescence in EMS lineage of GFP-tagged wild-type POP-1 and the indicated POP-1 mutants at a stage with two MS daughters (MSa, MSp; left-most pair) and two E daughters (Ea, Ep). A-P sisters in the same focal plane are joined by a white line. Embryos are oriented with anterior towards the left. The posterior sister of the posterior pair for embryos labeled T425A and T425D is not focused in the focal plane shown. (D) Higher magnification view of GFP fluorescence in typical wild-type anterior and posterior nuclei, compared with typical nuclei from the three indicated GFP-tagged POP-1 variants. Note the puncta observed in the wild-type anterior nucleus and the T425D nucleus. Scale bars: 10 γm in C; 1 γm in D.