Figure 1.
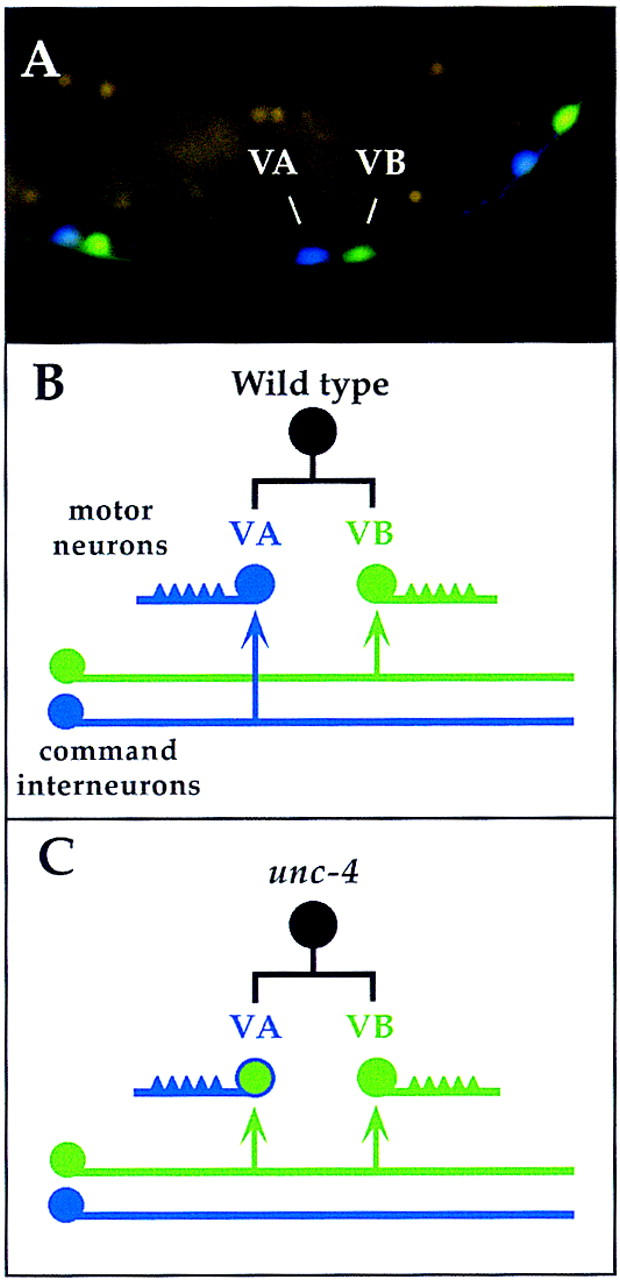
unc-4 specifies synaptic input to VA motor neurons. (A) Adjacent VA and VB motor neurons are visualized in this transgenic animal with neuron-specific promoters driving expression of the cyan GFP variant in VA motor neurons (unc-4::CFP) and the yellow GFP mutant protein in VB motor neurons (del-1::YFP) (Miller et al. 1999). (B) Most VA and VB motor neurons arise from a common precursor cell (black circle). In wild-type animals, VA neurons, which extend axons anteriorly, receive inputs from VA-type command interneurons (blue): AVA (chemical synapse and gap junction); AVD and AVE (chemical synapse). VB axons project posteriorly and are innervated by the VB-type interneurons (green): AVB (gap junction); PVC (chemical synapse). (C) In unc-4 mutants, VA neurons are miswired with VB-type inputs (i.e., form gap junctions with AVB). The arrows denote en passant synapses between side-by-side processes in the tightly packed ventral nerve cord and therefore are not indicative of axonal branches.
