Figure 5.
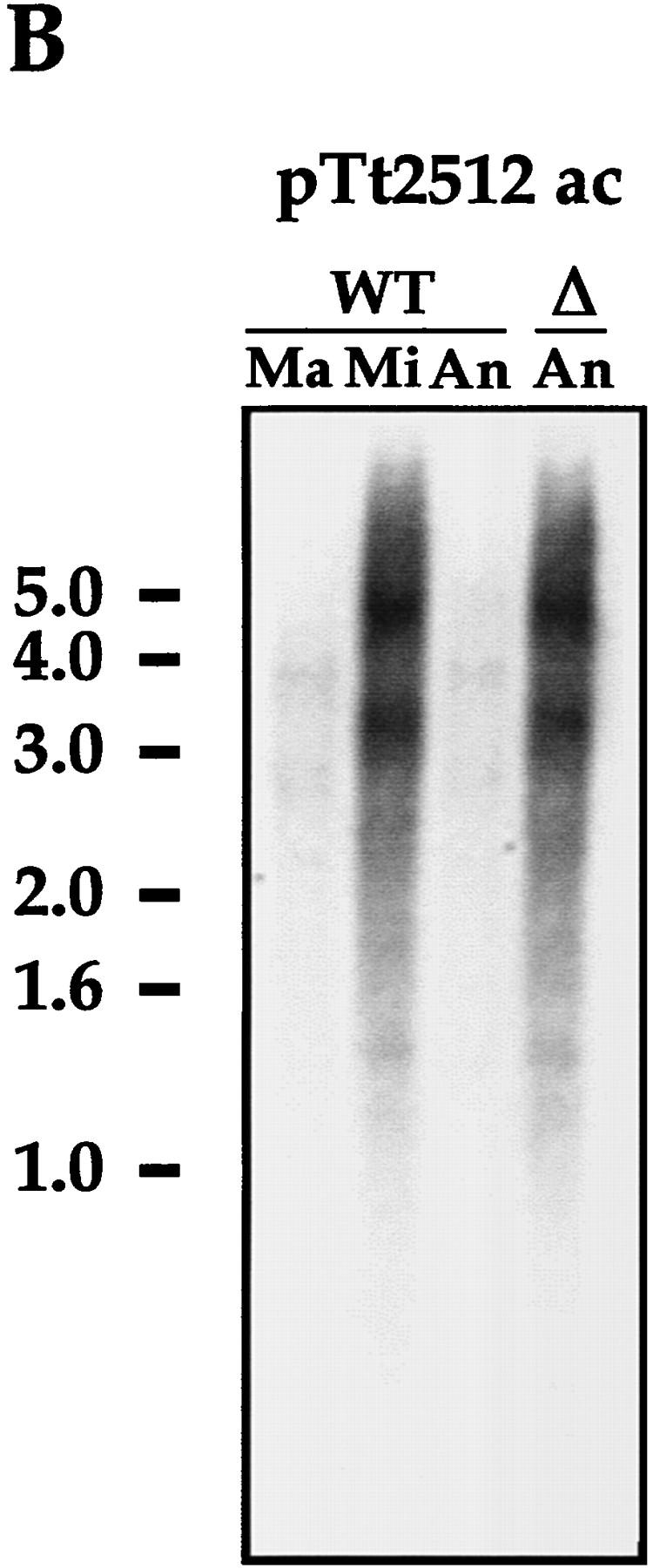
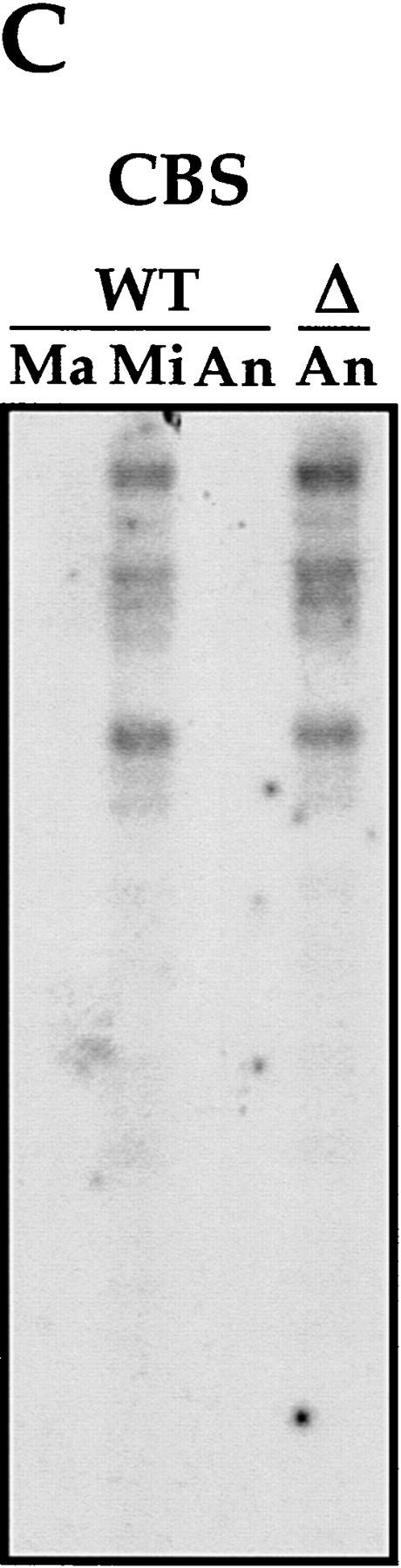
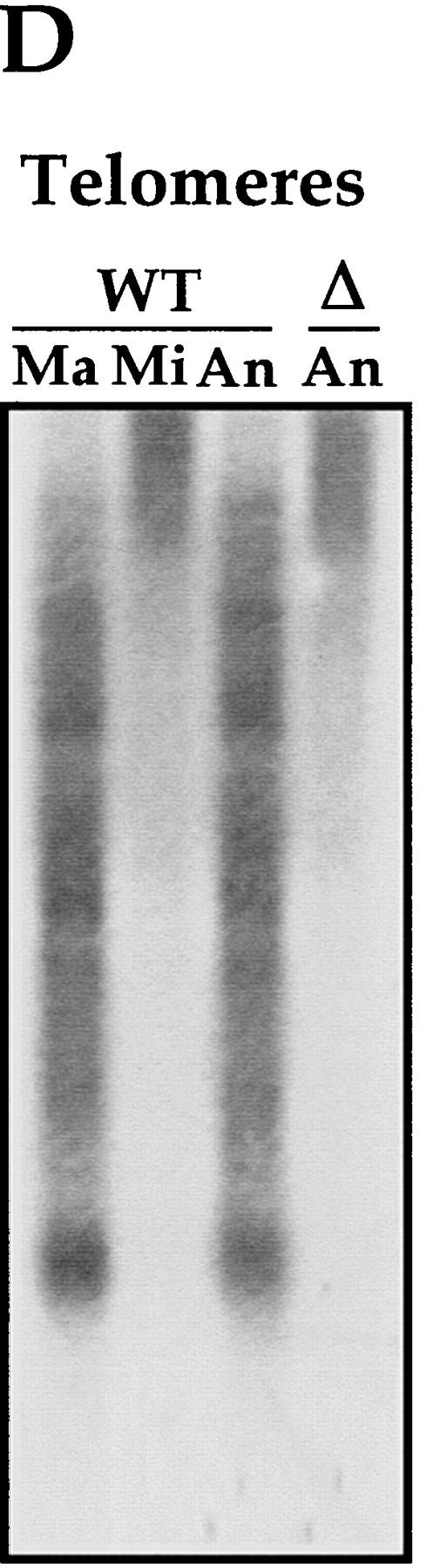
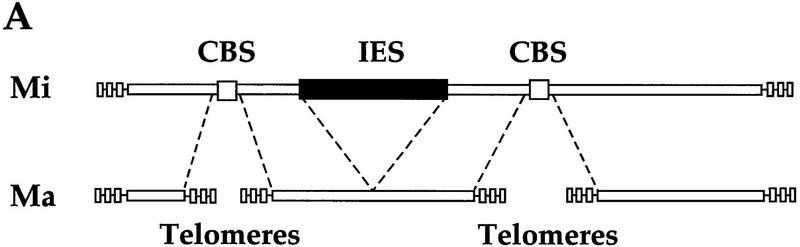
IES elimination, CBS elimination, and telomere addition are inhibited in PDD2 knockout cells. (A) Schematic representation of DNA rearrangements that occur during anlagen differentiation in wild-type cells. Open rectangles represent chromosomes, solid rectangles are IESs, open squares are CBSs; telomeres are shown as a group of rectangles. (Mi) Micronuclear chromosomes; (Ma) macronuclear chromosomes. (B–D) DNA (∼3 μg) isolated from macronuclei (Ma), micronuclei (Mi), or anlagen nuclei (An) from wild-type (WT) or mutant (Δ) cells was digested with HindIII enzyme and probed sequentially with the DNA sequences shown at the top of each blot. Anlagen from wild-type and mutant cells were isolated at 24 hr postmixing using sedimentation at unit gravity according to Allis and Dennison (1982). Purity of anlagen fractions was checked in Western blot analyses (not shown) using antibodies against micronuclear-specific linker histone (δ), a polypeptide known to be specific to micronuclei (Chicoine et al. 1985). DNA size standards are shown in kb.