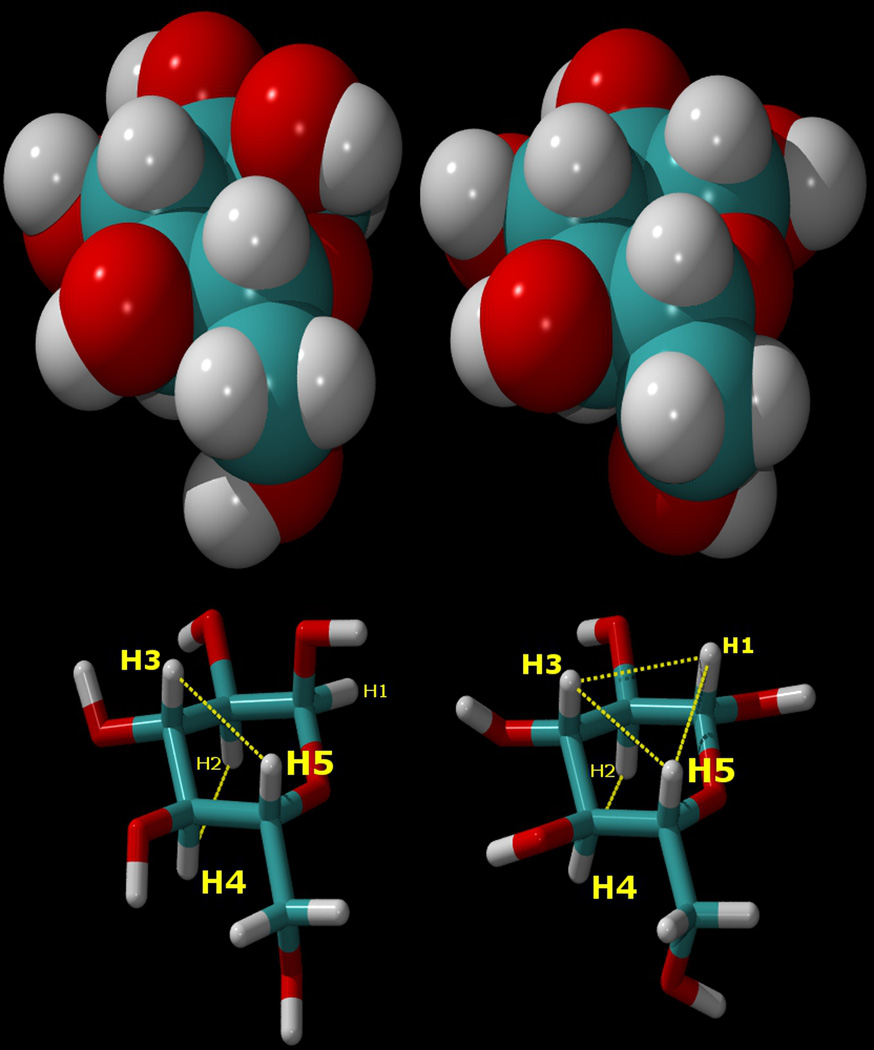
Figure 1.
Top: van der Waals surface representations of α-D-glucopyranose (left), and β-D-glucopyranose (right). Bottom: the atomic numbering for the atoms in these sugars, shown as “liquorice” drawings in the same orientations, and with the axial aliphatic protons connected by dotted lines to indicate their hydrophobic regions. As can be seen, the H1–H3–H5 “underside” of the β anomer is completely hydrophobic. In the α anomer (left), the positions of the hydroxyl group and proton on the C1 atom are interchanged, disrupting the aliphatic proton triad.