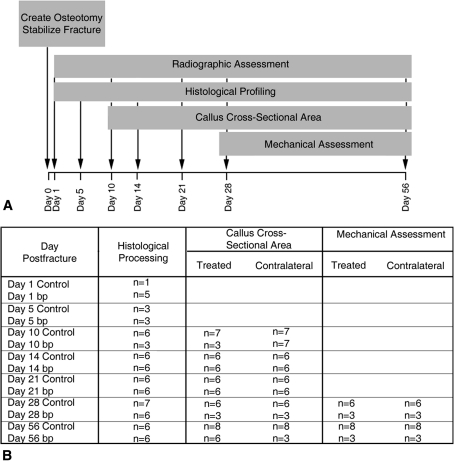
Fig. 1A–B.
(A) Using two independent groups, the contribution of GDF-5 to fracture healing was assessed by a tibial osteotomy model stabilized by intramedullary and extramedullary fixation. Healing fractures in 10-week-old male bp mice with a GDF-5 null mutation and their wild-type background counterparts were compared during 56 days of healing. Radiographs were obtained of all animals participating in the study on Days 1, 10, 21, 28, and 56 after osteotomy. The effect of GDF-5 contribution to repair was assessed by histologic profiling on Days 1, 5, 10, 14, 21, 28, and 56 postfracture. Callus cross-sectional area was quantified on Days 10, 14, 21, 28, and 56 postfracture and mechanical assessments were conducted at Days 28 and 56 postfracture. (B) The number of biological replicates used for each outcome measure varied depending on time and assessment.