Figure 1.
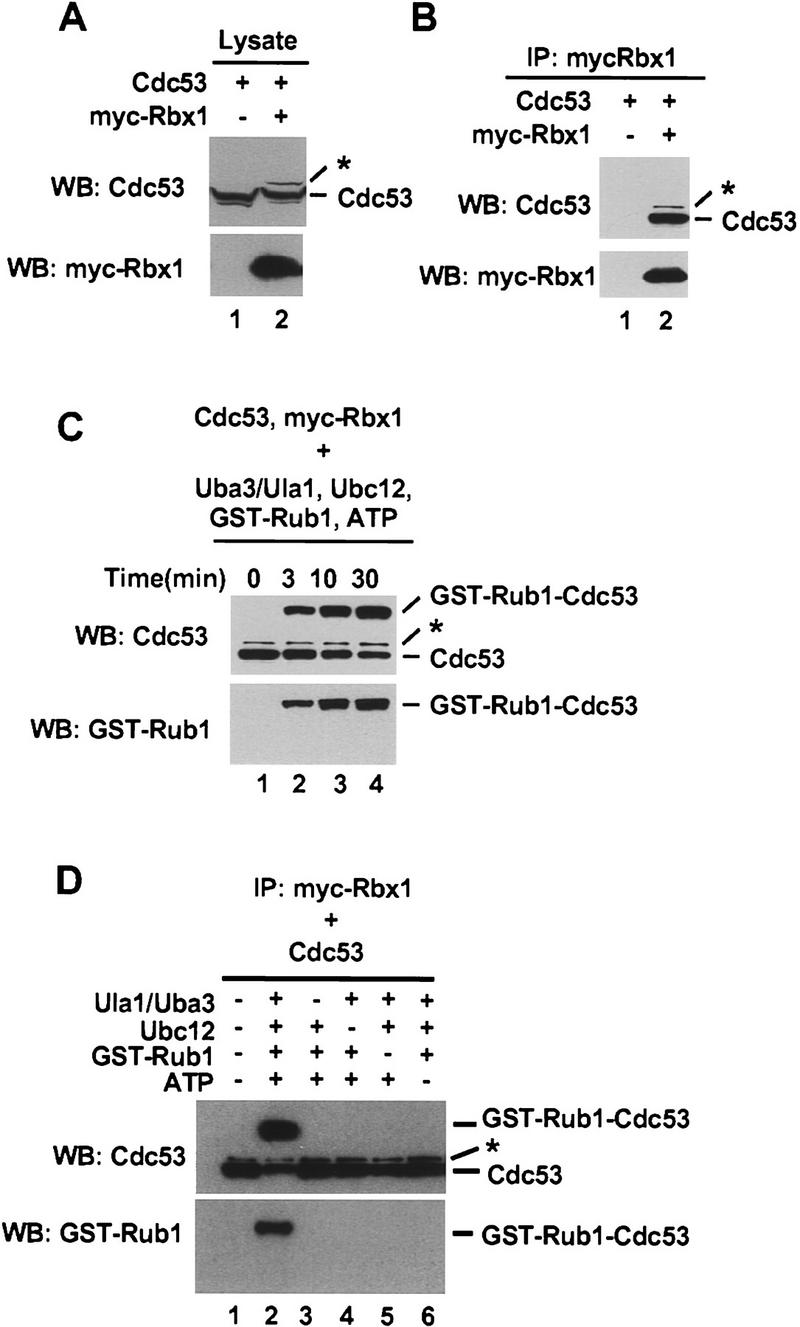
Conjugation of Rub1 to Cdc53 in vitro. (A) Total cell lysate (20 μg) from Sf21 cells infected with the indicated baculoviruses was immunoblotted with anti-Cdc53(yC-17) or anti-myc antibodies. (B) Total cell lysate (200 μg) from baculovirus-infected Sf21 cells was immunoprecipitated with 2 μg of anti-myc antibody and then immunoblotted with anti-Cdc53(yC-17) or anti-myc antibodies. (C) Total cell lysate (800 μg) from baculovirus-infected Sf21 cells was immunoprecipitated with 8 μg of anti-myc antibody. After immunoprecipitation, protein A Sepharose beads were divided into four tubes and and assayed for Rub1 conjugation activity at 25°C for the indicated times. Reaction products were immunoblotted with anti-Cdc53(yC-17) or anti-GST antibodies. (D) Total baculovirus-infected total cell lysate (1200 μg) was immunoprecipitated with 12 μg of anti-myc antibody. After immunoprecipitation, protein A Sepharose beads were divided into six tubes and assayed for Rub1 conjugation activity incubated at 25°C for 30 min in the presence or absence of Uba3/Ula1, Ubc12, GST–Rub1, and ATP as indicated and immunoblotted with anti–Cdc53(yC-17) or anti-GST antibodies. The asterisks (*) indicate a higher molecular mass Cdc53 species that is most likely conjugated to endogenous Rub1.
