Figure 3.
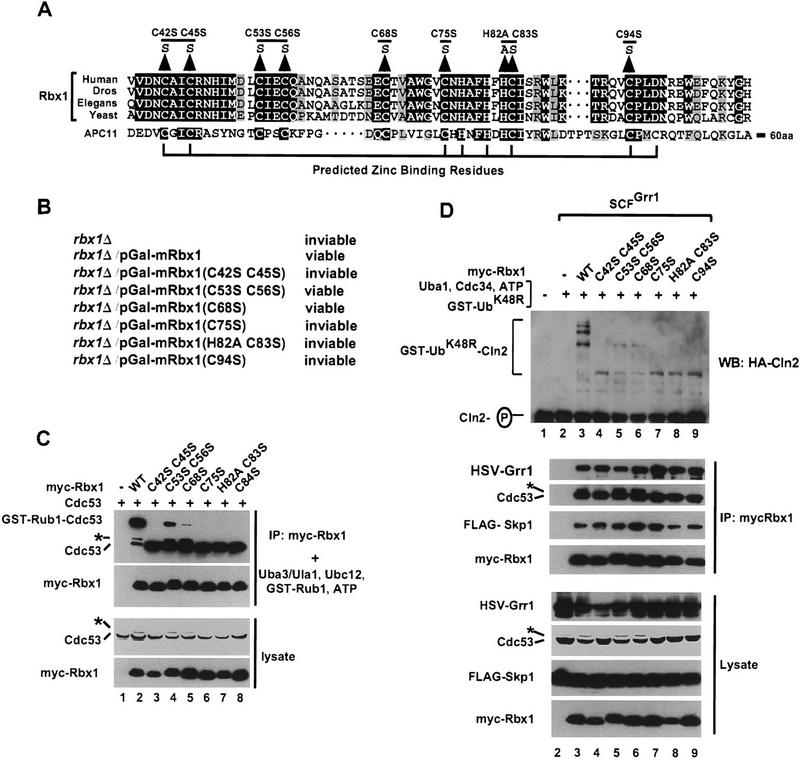
Mutation of predicted zinc-binding residues of Rbx1 is lethal in S. cerevisiae and interferes with Rbx1 activity in Rub1 conjugation and in ubiqutination of Cln2 by SCFGrr1. (A) Alignment of Rbx1 from human, Drosophila melanogaster (Dros), C. elegans (Elegans), or S. cerevisiae (Yeast) with APC11 from S. cerevisiae. (B) Effects of Rbx1 mutations on S. cerevisiae viability. (C) Cell lysate (200 μg) from Sf21 cells infected with the indicated baculoviruses was immunoprecipitated with 2 μg of anti-myc antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were assayed at 25°C for 50 min for Rub1 conjugation activity and reaction products were immunoblotted with anti-Cdc53(yC-17) or anti-myc antibodies (top panels). Cell lysate protein (20 μg) from the same cells was immunoblotted with anti-Cdc53(yC-17) or anti-GST antibodies (bottom panels). (D) Total cell lyaste (400 μg) from Sf21 cells infected with the indicated baculoviruses was immunoprecipitated with 4 μg of anti-myc antibody. One-half of the immunoprecipitate was immunoblotted with anti-HSV, anti-Cdc53(yC-17), anti-FLAG, or anti-myc antibodies (middle panels). The remaining immunoprecipitate was assayed for SCFGrr1 activity at 25°C for 60 min as described in Materials and Methods. Reaction products were immunoblotted with anti-HA antibody (top panel). The same cell lysates (20 μg) were immunoblotted with anti-HSV, anti–Cdc53(yC-17), anti-FLAG, or anti-myc antibodies (bottom panels).
