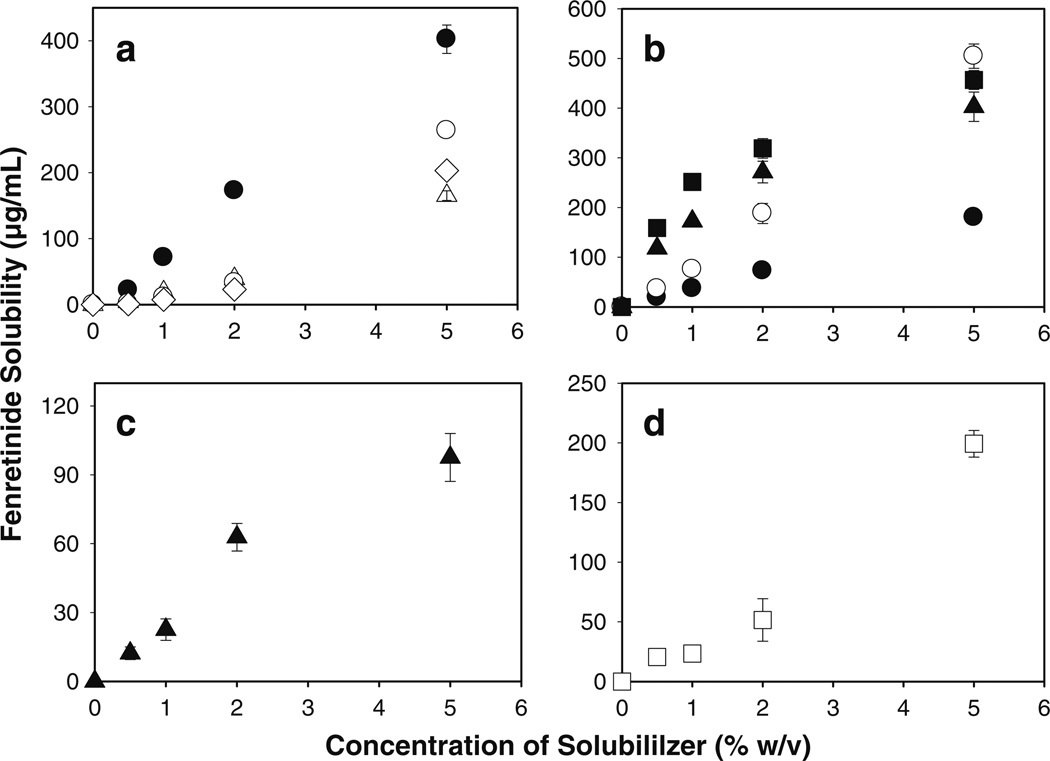
Fig. 2.
Significant enhancement of fenretinide solubility in simulated saliva (pH 6.8) by non-ionic surfactants, bile salts, phospholipid, and novel amphiphilic polymer. Effect of co-incorporation of 0.5–5%w/v bile salts (a: sodium deoxycholate (●), sodium cholate (○), sodium glycocholate (△), and sodium taurocholate (◊)), nonionic surfactants (b: Brij® 35 (●), Brij® 98 (○), Tween® 20 (▲), and Tween® 80 (■)), novel polymeric solubilizer (c: Soluplus®), and phospholipid (d: lecithin) on the solubility of fenretinide in simulated saliva. Studies were conducted in amber color ampoules under evacuated conditions at 37°C and symbols represent mean ± SE, n = 3.