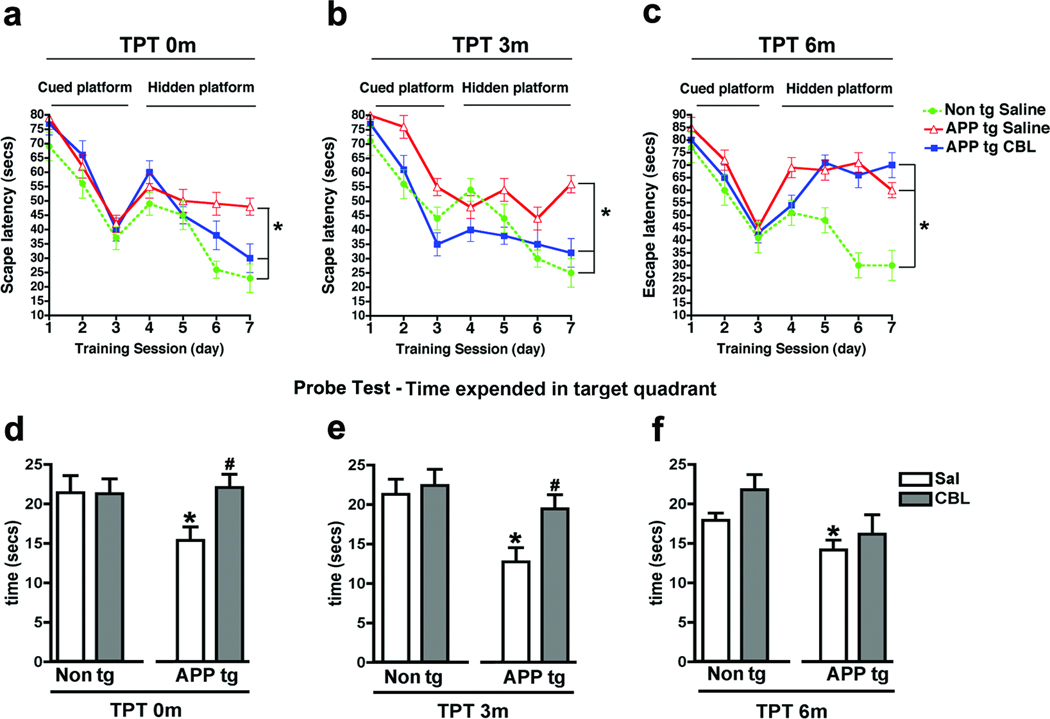
Fig 1. Behavioral deficits in the water maze 3 and 6 months after the cessation of CBL therapy in APP tg mice.
To evaluate the effect of CBL treatment interruption on memory and spatial learning APP tg mice were tested in the water maze. (a) Escape latency in the cued and hidden portions of the water maze in saline-treated non tg mice and saline or CBL-treated APP tg mice at TPT 0m. (b) Escape latency in the cued and hidden portions of the water maze in saline-treated non tg mice and saline or CBL-treated APP tg mice at TPT 3m. (c) Escape latency in the cued and hidden portions of the water maze in saline-treated non tg mice and saline or CBL-treated APP tg mice at TPT 6m. (d) Probe Test performance in saline or CBL-treated non tg or APP tg mice at TPT 0m. (e) Probe Test performance in saline or CBL-treated non tg or APP tg mice at TPT 3m and (f) Probe Test performance in saline or CBL-treated non tg or APP tg mice at TPT 6m. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. For (a–c) (*) Indicates p<0.05 by repeated-measures two-way ANOVA and (#) indicates p<0.05 when comparing CBL-treated APP tg mice with saline-treated APP tg mice by repeated-measures two-way ANOVA. For (d–f) (*) Indicates p<0.05, when comparing APP tg mice with saline-treated non tg mice by one-way ANOVA and (#) indicates p<0.05 when comparing CBL-treated APP tg mice with saline-treated APP tg mice by one-way ANOVA.