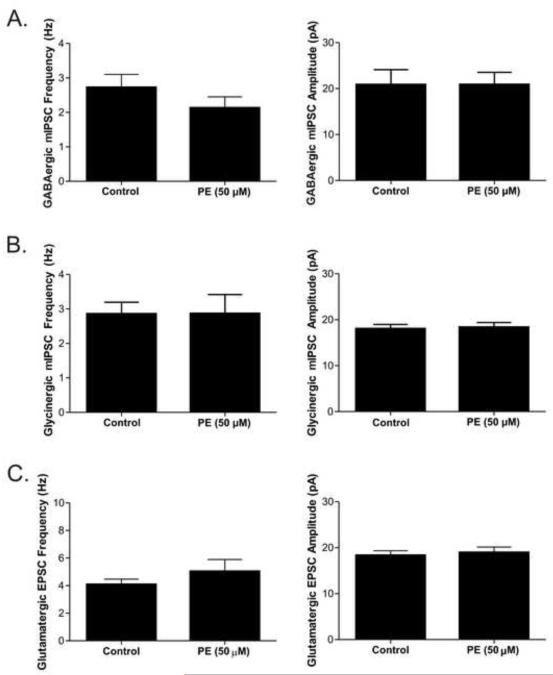
Figure 5. The selective α1-adrenergic receptor agonist phenylephrine (PE; 50 μM) was applied in the presence of the sodium channel blocker TTX (1 μM) to examine the potential mechanisms responsible for the increase in inhibitory neurotransmission to cardiac vagal neurons (CVNs) after α1-adrenergic receptors activation.
Control bath condition in A and B includes TTX which prevented the inhibition that occurred with α1-adrenergic receptor activation. A. The mean frequency and amplitude averages for GABAergic IPSCs (n=7). B. The mean frequency and amplitude averages for glycinergic IPSCs (n=8). C. The mean frequency and amplitude averages for glutamatergic EPSC after PE (n=9).