Figure 3.
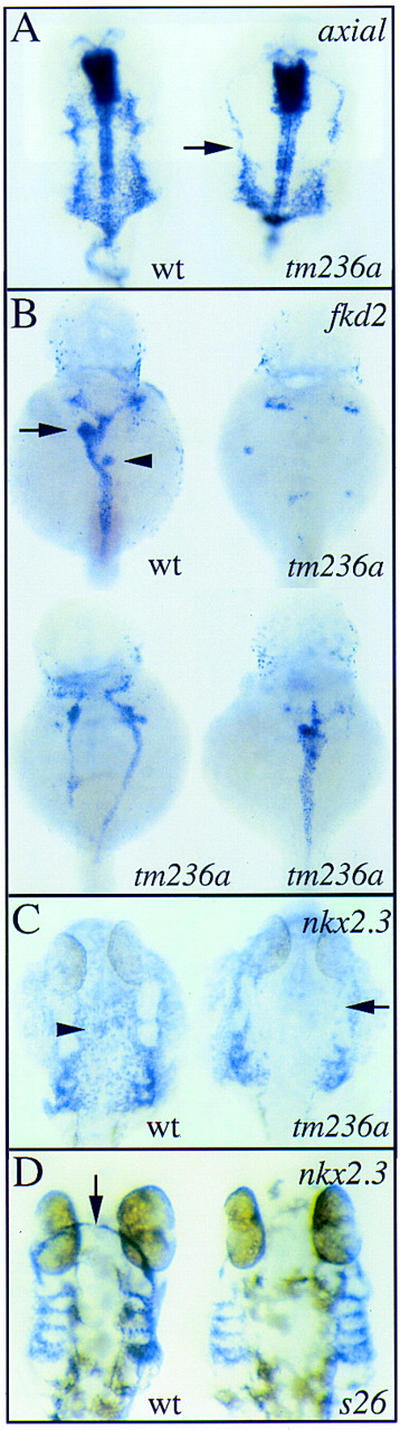
Endoderm development is abnormal in fau mutants. Expression of axial (A), fkd2 (B), and nkx2.3 (C,D) in wild-type embryos and fau mutant siblings at 44 hpf (A,B,D) and 28 hpf (C). All views are dorsal with anterior to the top. (A) axial is expressed in the anterior gut endoderm and the ventral neuroectoderm. At this stage, the anterior gut endoderm is coalescing at the embryonic midline in wild-type embryos. In fau mutants, gut endoderm is only present laterally (arrow). For purposes of orientation, the arrow is at the level of the midbrain–hindbrain boundary. (B) fkd2 is expressed throughout the pancreas (arrowhead), liver (arrow), and posterior gut tube in wild-type embryos. fau mutants display variable abnormalities in the morphogenesis and amount of fkd2-positive tissue. These defects range from near absence of fkd2-positive endoderm (top right) to formation of two lateral gut tubes (bottom left) to the absence of gut looping (bottom right). (C) Morphogenesis of the pharyngeal pouches is disrupted in fau mutants. The mediolateral distance between the pouches is greater in fau mutants and the anterior pouches (arrow) are disorganized. Also, midline nkx2.3-expressing cells (arrowhead) appear to be absent in fau mutants. (D) In faus26 mutants, the anterior domain of nkx2.3 expression (arrow) is absent.
