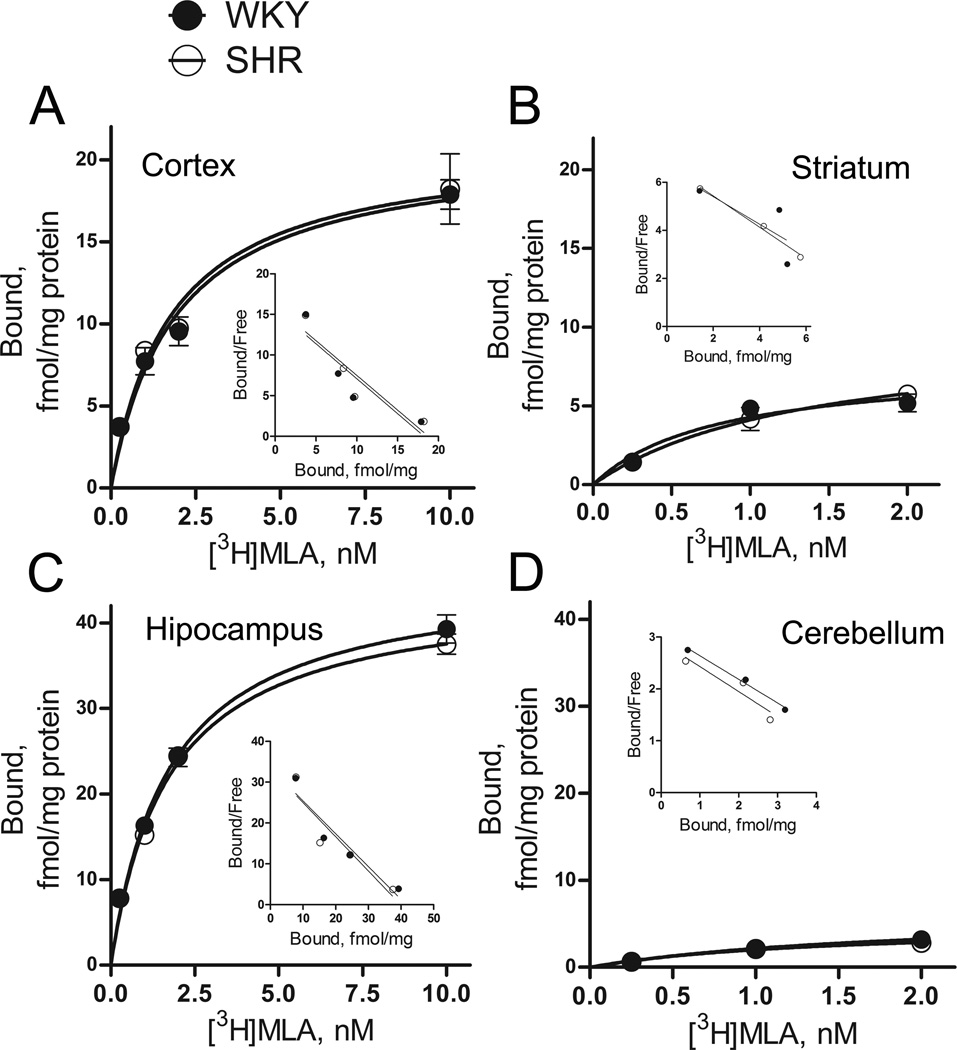
Figure 3.
Specific [3H]MLA binding to SHR and WKY membranes from cortex (A), striatum (B), hippocampus (C) and cerebellum (D). Corresponding Scatchard plots are shown in the inset. Both maximum binding sites (Bmax) and dissociation constants (Kd values) were unchanged in SHRs compared to WKY rats in all four brain regions. In cortex, Bmax values were 21.0 ± 1.9 and 20.9 ± 1.5 fmol/mg protein (p > 0.05), with Kd = 1.8 ± 0.5 and 1.9 ± 0.4 nM for SHR and WKY respectively (p > 0.05). In striatum, Bmax values were 9.8 ± 2.6 and 7.6 ± 1.4 fmol/mg protein (p > 0.05), with Kd = 1.4 ± 0.7 and 0.8 ± 0.4 nM for SHR and WKY respectively (p > 0.05). In hippocampus, Bmax values were 44.0 ± 1.7 and 45.8 ± 1.7 fmol/mg protein (p > 0.05), with Kd = 1.7 ± 0.2 and 1.7 ± 0.2 pM for SHR and WKY respectively (p > 0.05). In cerebellum, Bmax values were 4.9 ± 2.5 and 6.2 ± 5.2 fmol/mg protein (p > 0.05), with Kd = 1.4 ± 1.4 and 1.9 ± 2.8 nM for SHR and WKY respectively (p > 0.05). Membranes (~0.6 mg protein) and [3H]MLA were incubated for 1.5 hours at 23°C. Non-specific binding was determined in the presence of 1 mM nicotine. Each data point represents mean ± SEM of 3 to 4 rats.