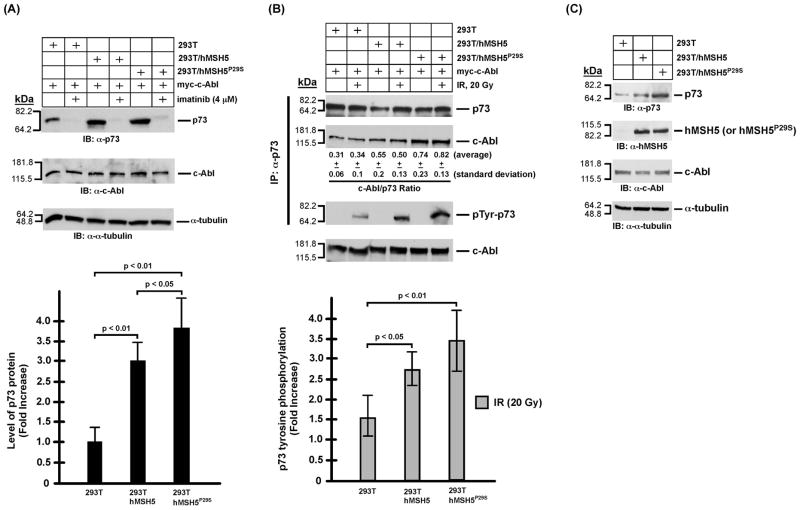
Figure 4.
Analysis of p73 protein accumulation and phosphorylation in 293T, 293T/hMSH5, and 293T/hMSH5P29S cells. It is known that both p73αand p73β are stabilized by c-Abl and both undergo c-Abl dependent tyrosine phosphorylation in response to IR, of which p73β was particularly examined in these experiments [20,28,29]. (A) Immunoblotting analysis of p73 accumulation in 293T, 293T/hMSH5, and 293T/hMSH5P29S cells. Blots of α-tubulin and c-Abl were used as loading controls. Levels of p73 protein was determined from at least three experiments and quantified for the relative increases of p73 accumulation above that of the untreated 293T cells. Error bars are standard deviation from the mean (bar graph, lower panel). (B) Analysis of the interaction between p73 and c-Abl, as well as p73 tyrosine phosphorylation 1 h after IR exposure. 293T, 293T/hMSH5, and 293T/hMSH5P29S cells were transfected to express myc-c-Abl prior to exposure to 20 Gy IR. Co-IP was performed with α-p73 and the resulting immunoprecipitates were used to analyze the amounts of p73 and c-Abl proteins as well as the status of p73 tyrosine phosphorylation. The average c-Abl/p73 ratios (representing the relative levels of these two proteins in the immunoprecipitates) and standard deviations were determined by three immunoblotting analyses of immunoprecipitates. The status of IR-triggered p73 tyrosine phospho-rylation was determined by the use of the α-p-Tyr antibody. The average levels of p73 phospho-rylation and corresponding standard deviations (error bars) were determined in three measurements (bar graph, lower panel). The levels of c-Abl in cell extracts are also shown. (C) Immunoblotting analysis of untransfected and untreated 293T, 293T/hMSH5, and 293T/hMSH5P29S cells. kDa, molecular weight (Mr) in thousands.