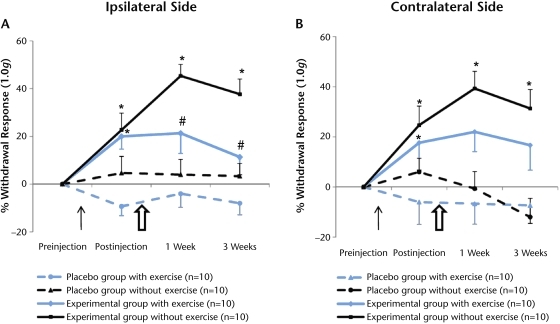
Figure 1.
Effect of moderately intense exercise on cutaneous hyperalgesia. Acidic saline injections significantly increased cutaneous withdrawal responses on the ipsilateral and contralateral sides. (A) Moderately intense exercise significantly decreased withdrawal responses at 1-week and 3-week time points on the ipsilateral side (P<.05). (B) A similar effect of exercise was noted on the contralateral side, but it was not significant (P>.05) at any time points. The thin black arrow indicates the injection of acidic or normal saline. The larger, open arrow indicates the initiation of exercise training. Data are represented as change in mean score from before injection to each time point; error bars indicate standard error of the mean. * denotes status of hypersensitivity and P<.05 for difference between experimental and placebo groups (acidic versus normal saline) at the postinjection time points. # denotes effects of exercise training and P<.05 for difference between exercise and no-exercise groups at the postexercise time points.