Figure 1.
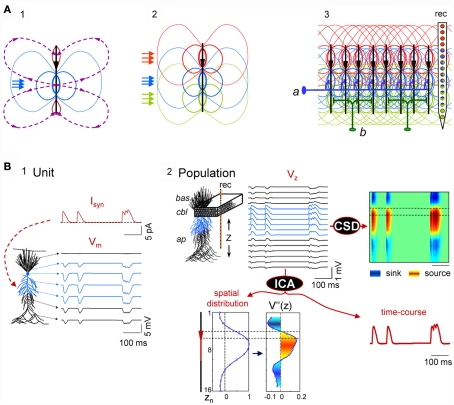
Scaling single neuron currents to macroscopic LFPs and their separation by independent component analysis (ICA). (A) The problem of the mixing of currents in the volume constituting LFPs is simplified in regular structures. A synaptic input to a single neuron (blue arrows in subplot 1) produces quadrupole-like extracellular fields (blue and red isopotential curves) and currents (dashed curves). Due to the spread of currents in the extracellular volume, the field potentials generated by several synapses in different domains overlap strongly (panel 2), but in regular structures with stratified inputs the simultaneous activation of many neurons produce laminar field potentials that are specific for each input (panel 3), and they can be captured by fix groups of electrodes within linear recording arrays (rec). a and b schematically illustrate the multicellular connection of axons from extrinsic neurons and local interneurons, respectively. (B) An irregular series of inhibitory synaptic currents (panel 1, unit, Isyn) is injected to a dendritic band (blue compartments) of one model neuron enabling the calculation of the compartmental membrane potentials (Vms) and currents (Ims) along the neuron anatomy. The Ims of the single neuron are replicated in a CA1 aggregate (subplot 2, population) of model neurons to build the LFPs, which were estimated along a 16-point recording track (rec). LFPs are stratified along the main Z-axis of single units (VZ) and they can be analyzed by current-source density analysis (CSD), or decomposed into their contributing generators by ICA. The ICA reports only one generator, with its spatial distribution and time course. The second spatial derivative of the spatial distribution, V”(z), renders the location of active currents (in yellow/red), which match the locus of activated synapses. The time course of the ICA-derived LFP-generator precisely matches the injected synaptic current on each single neuron. Cbl, cell body layer; bas, basal dendrites; ap, apical dendrites.