Figure 5.
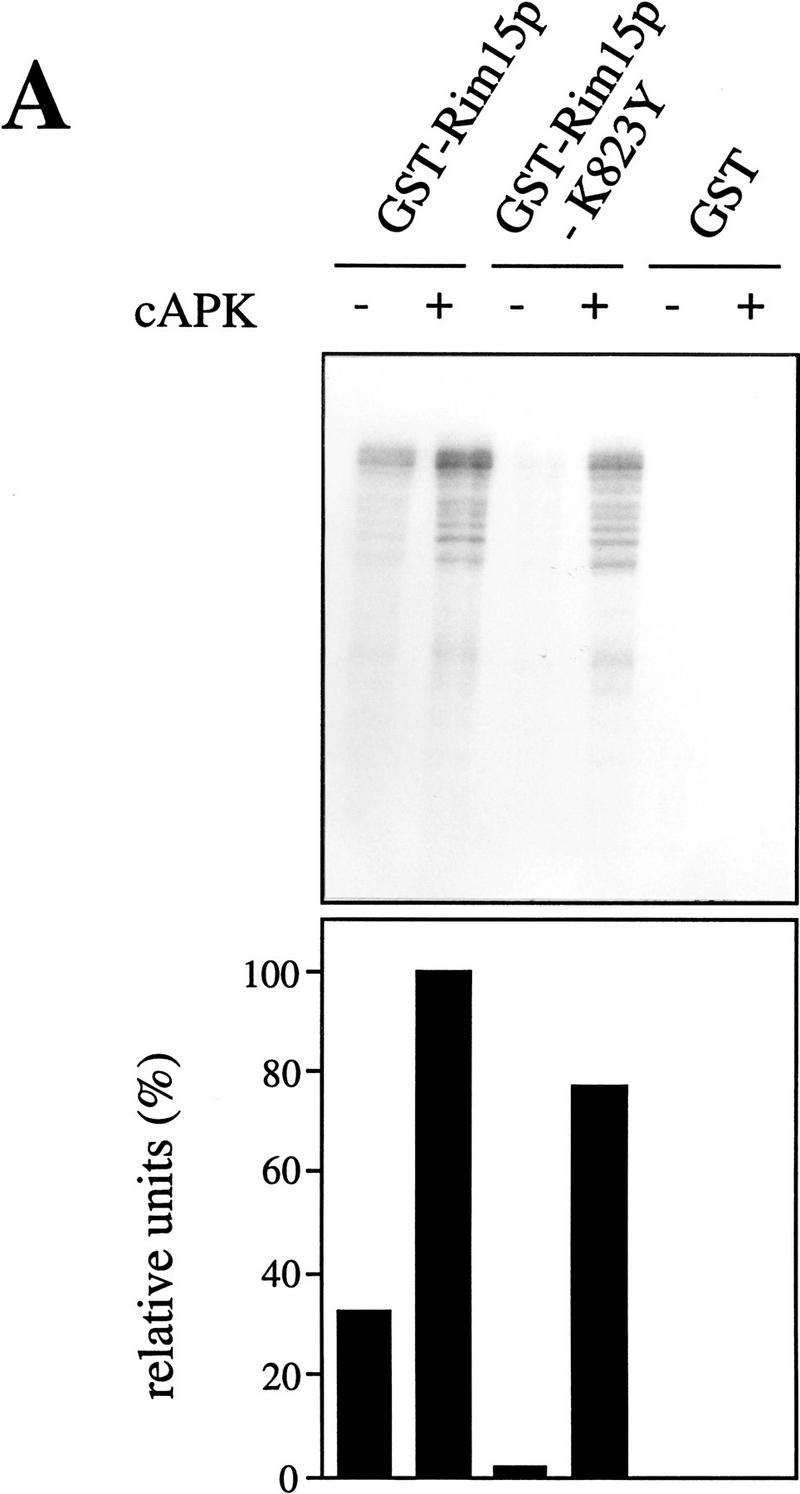
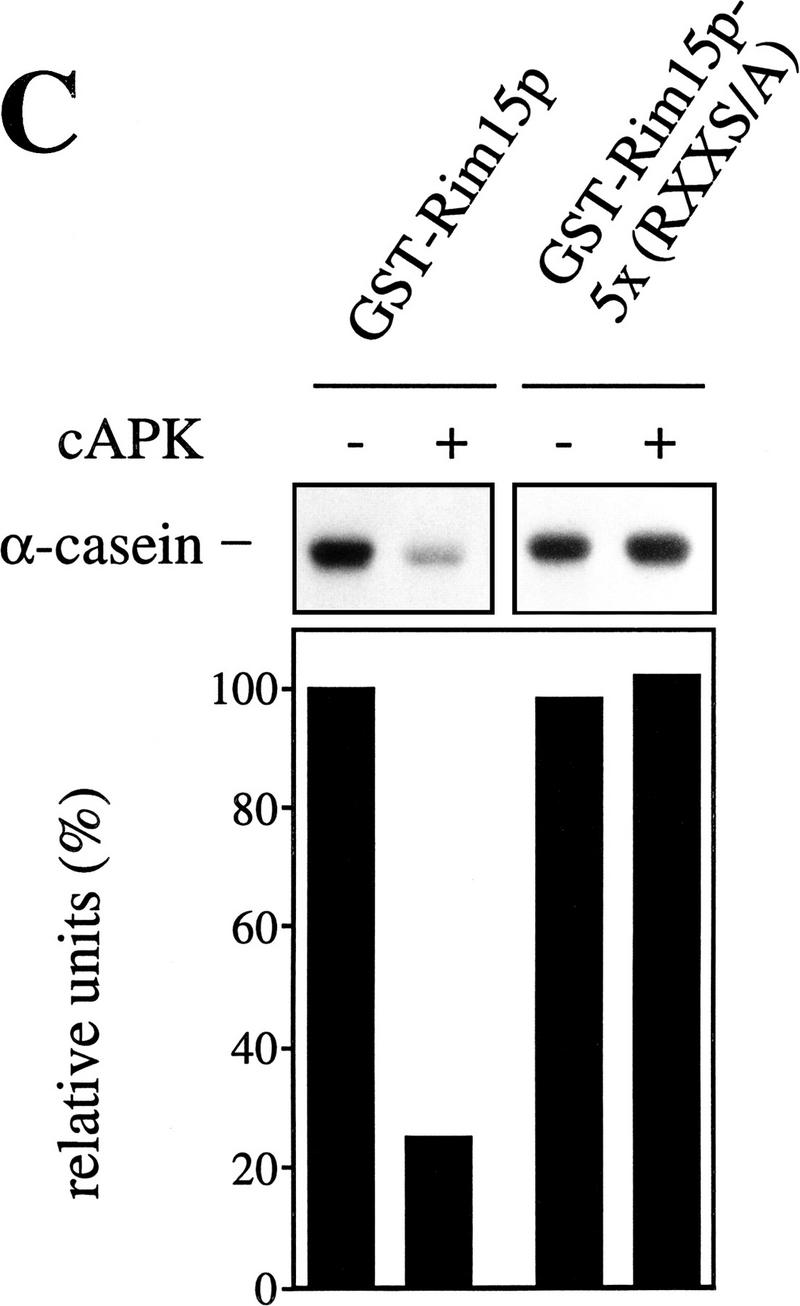
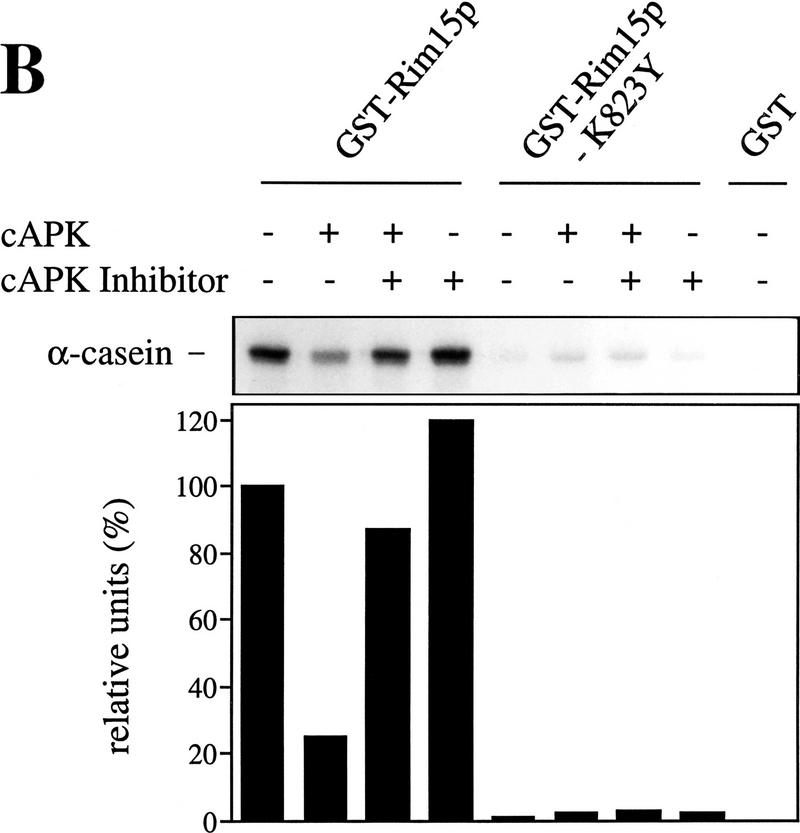
cAPK-dependent phosphorylation of Rim15p inhibits its kinase activity. (A) GST–Rim15p, GST–Rim15p-K823Y, and GST proteins were purified and analyzed for autophosphorylation activity and their potential to be phosphorylated by cAPK. Accordingly, equal amounts of the fusion proteins (verified by immunoblotting with anti-GST antibodies) were incubated with [γ-32P]ATP either in the absence (−cAPK) or in the presence (+cAPK) of cAPK as described in Materials and Methods. Phosphorylation levels were quantitated by PhosphorImager analysis and expressed as percent of the GST–Rim15p-phosphorylation level (+cAPK). (B) To analyze the effect of cAPK-dependent phosphorylation of Rim15p, equal amounts of GST–Rim15p, GST–Rim15p-K823Y, and GST (verified by immunoblotting as in A) were preincubated with unlabeled ATP and either no further additions, with cAPK, with cAPK and cAPK inhibitor, or with cAPK inhibitor alone, as indicated. The samples were washed extensively and assayed for α-casein phosphorylation in the presence of cAPK inhibitor and [γ-32P]ATP. The levels of α-casein phosphorylation were quantitated by PhosphorImager analysis and expressed as percent of the control (level of α-casein phosphorylation after preincubation of GST–Rim15p in the absence of both cAPK and cAPK inhibitor). (C) Equal amounts of GST–Rim15p and GST–Rim15p-S709A/S1094A/S1416A/ S1463A/S1661A [GST–Rim15p-5x(RRXS/A)] were analyzed as in B.