Fig. 1.
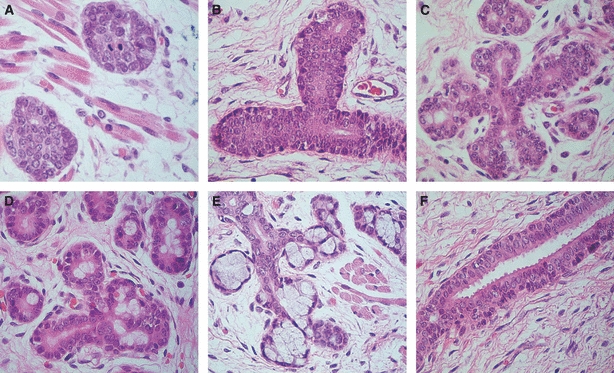
Morphological phases of human salivary gland development. (A) Initial bud: solid nests of epithelial cells surrounded by a loose mesenchyme (original magnification ×400). (B) Pseudoglandular stage: solid cords of epithelial cells with central vestigial luminal spaces (original magnification ×400). (C) Canalicular stage: proliferation of the glandular structure, forming a complex network of canalized structures (original magnification ×400). (D) Terminal bud – initial stage: presence of terminal bulbs composed of cells with large and clear cytoplasm (original magnification ×400). (E) Terminal bud – advanced stage: presence of well established acinar lobules (original magnification ×400). (F) Well developed excretory duct composed of multiple layers of epithelial cells. Note the secretion of eosinophilic material (mucous material) on the luminal pole of luminal cells (original magnification ×400).
