Figure 2.
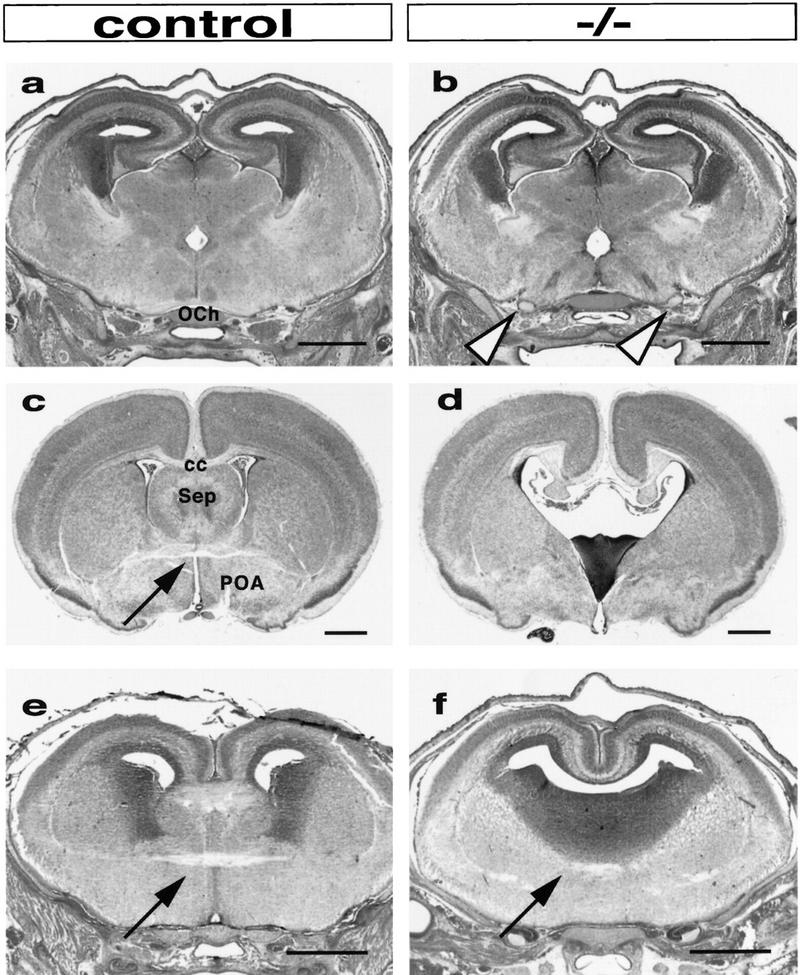
Growth and cell differentiation are deficient in the medioventral forebrain of homozygous Vax1 mutants. (a,b,e,f) 16.5-dpc embryos, hematoxylin–eosin staining; (c,d) P15 brain, cresyl violet staining. The optic chiasm (a, OCh) was systematically absent from homozygous animals so that the mutant optic nerves (arrowheads in b) entered the brain at a lateral hypothalamic level. The telencephalic phenotype of Vax1 homozygous mutants ranged from a total absence of growth of medioventral structures, including the septum (Sep) and preoptic area (POA) (c,d) to a growth–recovery of dorsolateral structures fusing medially (e,f). In this latter case only, fibers crossing the midline may be observed at the anterior commissure level (arrows in c,e,f). The medioventral growth defects resulted in lobar holoprosencephaly (d,f). Bar, 0.5 mm.
