Figure 4.
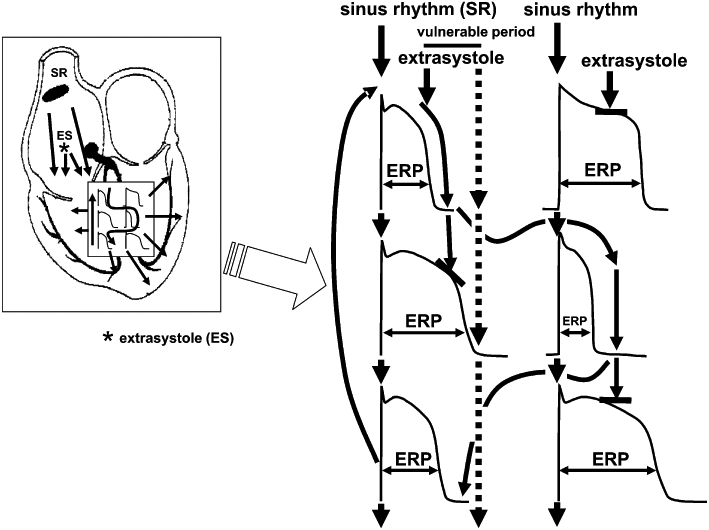
The simplified illustration of the mechanism of arrhythmia development due to lengthening of repolarization and decreased repolarization reserve leading to enhanced spatial repolarization heterogeneity. When the duration of repolarization and therefore the refractory period are prolonged in a heterogenous fashion, that is, the intrinsic transmural/regional repolarization heterogeneities are further augmented by repolarization reserve impairment in cells/regions in a different degree, an arrhythmia substrate is created. An extra stimulus in the vulnerable period then can travel back in a complicated path to its site of origin due to enhanced differences in refractoriness of myocardial cells leading to serious ventricular arrhythmia. Dotted arrows show an extra stimulus occurring after the vulnerable period propagating on the physiological path not leading to serious arrhythmia. ERP, effective refractory period.
