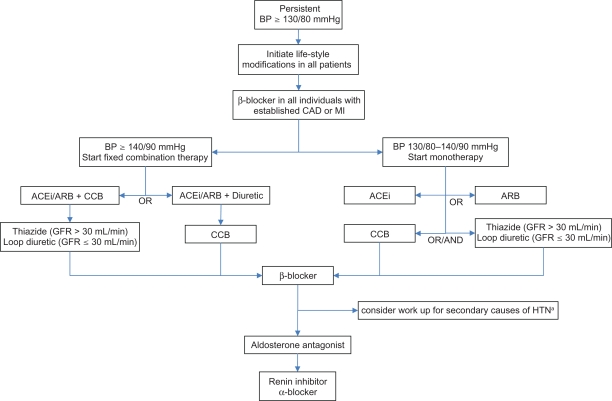
Figure 1.
Algorithm for treatment of hypertension in inividuals with diabetes. Maximize dose before starting the next drug.
- Both reduce microalbuminuria and rate of nephropathy independently of their antihypertensive effect.
- Diuretic preferred in heart failure or edematous conditions.
- Loop diuretic recommended if GFR ≤ 30 mL/min due to marked state of fluid overload.
- If needed, CCB and diuretic can be combined.
Third line = β-blocker, primarily due to side effect profile. However, it is indicated in all patients with established CAD and MI.
Fourth line = Aldosterone antagonist (ASCOT-BPLA86).
Fifth line = Renin inhibitor or α-blocker, not enough comparative data from clinical trials for clear recommendation.
Peripheral α-blocker, due to orthostatic hypotension and results of ALLHAT.78 It could be used earlier in patients with symptomatic BPH.
arenal artery stenosis, hyperaldosteronism, Cushing’s syndrome or pheochromocytoma.
Abbreviations: BP, blood pressure; ACEi, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; CCB, calcium channel blocker; CAD, coronary artery disease; MI, myocardial infarction; HTN, hypertension; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; BPH, benign prostate hyperplasia.