Figure 4.
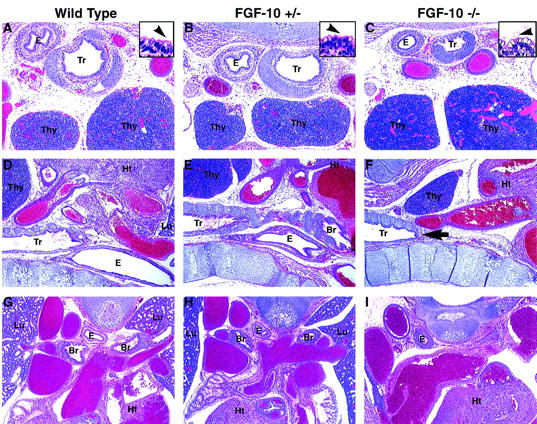
H&E-stained sections of E17.5 Fgf-10−/− fetuses (C,F,I) with Fgf-10+/+ (A,D,G) and Fgf-10+/− (B,E,H) littermates for comparison. (A–C) Fetal cross sections showing that Fgf-10−/− fetuses have a normal trachea (Tr) and thymus (Thy). (Insets in A–C) The tracheal epithelium from Fgf-10−/− fetuses is ciliated pseudostratified columnar (inset arrowheads indicate cilia) with mucus-secreting goblet cells (clear areas) and is morphologically identical to tracheal epithelium in wild-type and heterozygous fetuses. (D–F) Fetal sagittal sections showing that the Fgf-10−/− fetal trachea terminates blindly just beyond the anterior thymus (arrow in F), whereas the tracheas in wild-type and heterozygous fetuses continue beyond the thymus and branch to form main-stem bronchi (E). (G–I) Fetal cross sections showing that Fgf-10−/− fetuses (I) fail to develop main-stem bronchi (Br) or lungs (Lu). (E) Esophagus; and (Ht) heart in A–I.
