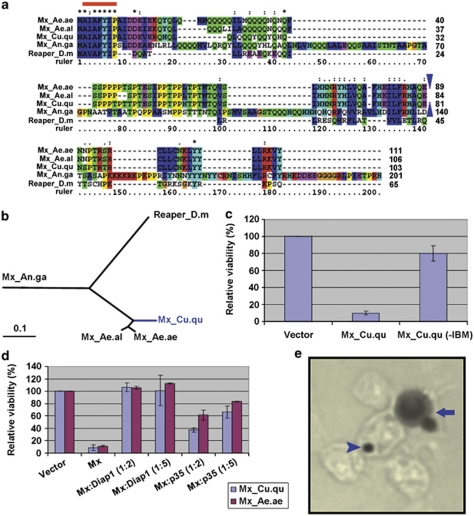
Figure 1.
Gene cloning and characterization of mx_Cu.qu. (a) Alignment of protein sequences of Mx orthologs in mosquitoes and Reaper from D. melanogaster. The blue triangles denote the relative position of the intron in Mx sequences (there is no intron in Reaper). The three Mx orthologs from Culicinae share considerable similarity besides the IBM (red line). However, they share little similarity with Mx from Anopheles or the Drosophila Reaper. (b) Distance tree of these orthologs. (c) Expression of Mx_Cu.qu kills C6/36 cells. However, when amino acids 2–4 are removed (−IBM), the protein has little, if any, proapoptotic activity. (d) Mx_Cu.qu-induced cell death is almost completely blocked by co-transfection of Diap1 and significantly inhibited by co-transfection of p35. Numbers in parentheses denote the ratio of respective genes. (e) C6/36 cells killed by expression of mx_Cu.qu or mx_Ae.ae show typical apoptotic morphology including cell fragmentation (arrow) and phagocytosis by neighboring cells (arrow head). Cells co-transfected with pIE-lacZ and pIE-mx_Cu.qu were fixed 20 h later and processed for X-Gal staining