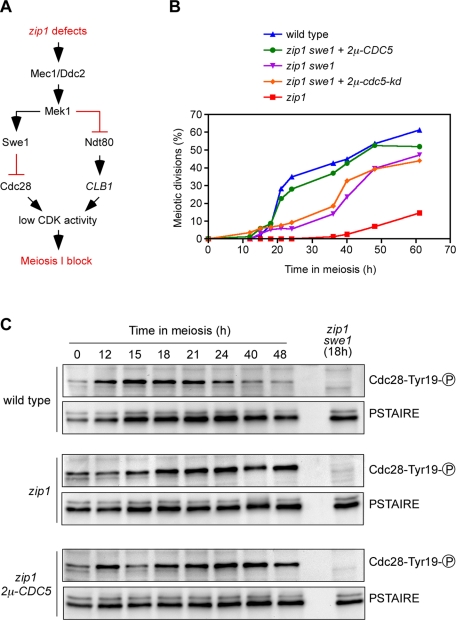
FIGURE 3:
Bypass of zip1 meiotic delay by high levels of active Cdc5 does not result from altered Swe1 function. (A) Schematic representation of the two regulatory branches targeted by the meiotic recombination checkpoint to restrain CDK activity, thus preventing meiosis I entry. Note that the positive and negative arrows connecting Mek1 to Swe1 and Ndt80, respectively, do not necessarily imply direct action. (B) Time course of meiotic nuclear divisions; the percentage of cells containing more than two nuclei is represented. Strains are wild type (DP396/pRS426), zip1 swe1 + 2μ-CDC5 (DP393/pJC29), zip1 swe1 (DP393/pRS426), zip1 swe1 + 2μ-cdc5-kd (DP393/pSS127), and zip1 (DP386/pRS426). (C) Swe1-dependent inhibitory phosphorylation of Cdc28 is not affected by Cdc5 overproduction. Western blot analysis of phosphorylation of Cdc28 at tyrosine 19 and total Cdc28 (PSTAIRE) throughout meiosis in wild type (DP396/pRS426), zip1 (DP386/pRS426), and zip1 2μ-CDC5 (DP386/pJC29). Extracts from a zip1 swe1 strain (DP393), which lacks Cdc28Tyr19 phosphorylation, were used as control for specificity of the antibody.