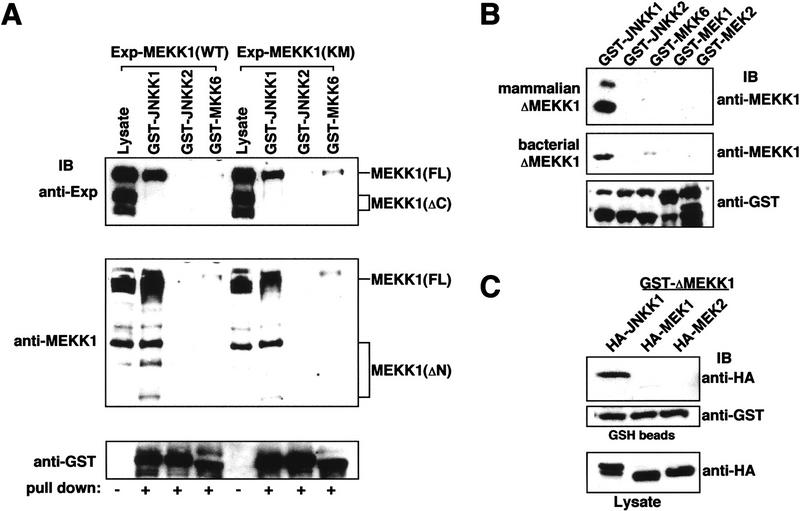
Figure 4.
MEKK1 binds to JNKK1. (A) Full-length MEKK1 specifically interacts with JNKK1 through its carboxy-terminal kinase domain. GST–MAPKK fusion proteins were expressed in E. coli and purified. Equal amounts of each protein were mixed with lysates of transfected Cos-1 cells containing transiently expressed wild-type (WT) or catalytically inactive (KM) MEKK1 with an amino-terminal Express epitope. The proteins were precipitated with GSH–Sepharose and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Express (top), anti-MEKK1 directed against the carboxy-terminal kinase domain (middle), or anti-GST (bottom). (B) Purified recombinant JNKK1 specifically and directly interacts with MEKK1. Purified, recombinant GST–MAPKK fusion proteins were mixed with lysates of cells expressing ΔMEKK1 (top) or with purified His–ΔMEKK1 expressed in E. coli (middle). The proteins were precipitated with GSH–Sepharose and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-MEKK1 or anti-GST (bottom). (C) Binding of JNKK1 to purified ΔMEKK1. Purified recombinant GST–ΔMEKK1 was mixed with Cos-1 cell lysates containing equal amounts of transiently expressed HA–JNKK1, HA–MEK1, or HA–MEK2 determined by anti-HA immunoblotting (bottom). The proteins were precipitated with GSH–Sepharose and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA (top) or anti-GST (middle).