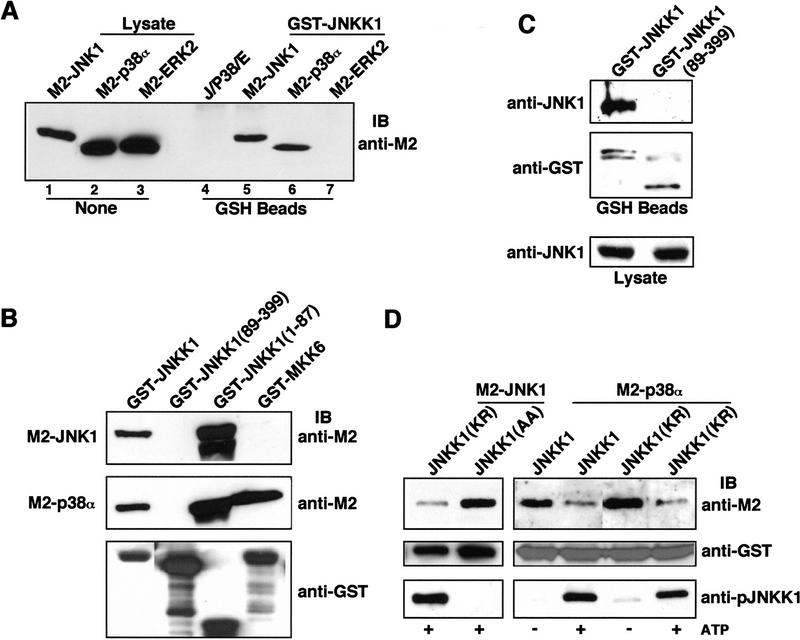
Figure 6.
JNKK1 specifically interacts with JNK1 and p38α. (A) JNKK1 stably interacts with JNK1 and p38α, but not with ERK2. Lysates (10 μg) of Cos-1 cells transfected with M2-tagged MAPK vectors were examined for MAPK expression by immunoblotting with anti-M2 (lanes 1–3). Lysates (400 μg) were also mixed with lysates containing GST–JNKK1, precipitated with GST–Sepharose, and immunoblotted with anti-M2. In addition, equal amounts of lysates containing each of the MAPKs were mixed and examined for binding to GSH–Sepharose in the absence of GST–JNKK1 (lane 4). (B) JNKK1 interacts with both JNK1 and p38α through its amino-terminal extension. Lysates containing M2–JNK1 or M2–p38α were mixed with purified, recombinant GST–JNKK1, GST–JNKK1(89–399), GST–JNKK1(1–87), or GST–MKK6. After precipitation with GSH–Sepharose and separation by SDS-PAGE, the precipitated proteins were immunoblotted with anti-M2 (top two panels) or anti-GST (bottom panel). (C) JNKK1 binds endogenous JNK1. HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with either GST–JNKK1 or GST–JNKK1(89–399) expression vectors. Cell lysates were prepared, precipitated with GSH–Sepharose, separated by SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotted with anti-JNK1 or anti-GST. A small fraction (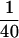 ) of each lysate was directly analyzed for its content of JNK1. (D) Lysates of Cos-1 cells expressing GST–JNKK1, GST–JNKK1(KR), or GST–JNKK1(AA) were incubated with a small amount of lysate containing ΔMEKK1 in kinase buffer in the absence or presence of 1 mm ATP. Then, lysates containing similar amounts of M2–JNK1 (left panels) or M2–p38α (right panels) were added. The mixtures were precipitated with GSH–Sepharose followed by immunoblotting with anti-M2 (top panels), anti-GST (middle panels), or anti-phospho-JNKK1 (bottom panels).
) of each lysate was directly analyzed for its content of JNK1. (D) Lysates of Cos-1 cells expressing GST–JNKK1, GST–JNKK1(KR), or GST–JNKK1(AA) were incubated with a small amount of lysate containing ΔMEKK1 in kinase buffer in the absence or presence of 1 mm ATP. Then, lysates containing similar amounts of M2–JNK1 (left panels) or M2–p38α (right panels) were added. The mixtures were precipitated with GSH–Sepharose followed by immunoblotting with anti-M2 (top panels), anti-GST (middle panels), or anti-phospho-JNKK1 (bottom panels).