Figure 4.
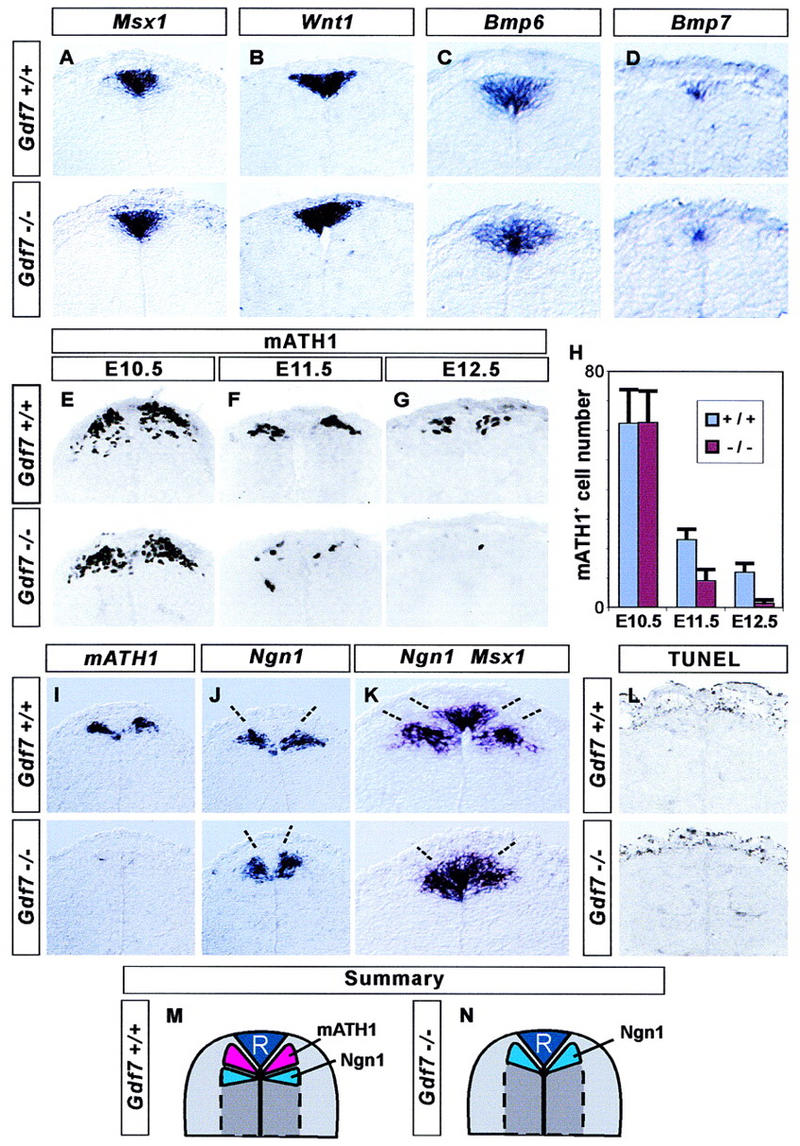
Loss of late mATH1+ progenitors in Gdf7 mutant mice. The development of roof plate cells and dorsal neural progenitors in the cervical (forelimb level) spinal cord in wild-type (top panels) and in Gdf7m1 homozygous mutant embryos (bottom panels). (A–D) In situ hybridization showing that roof plate expression of Msx1 (A), Wnt1 (B), Bmp6 (C), and Bmp7 (D) is normal in Gdf7 mutant embryos examined at E12.5 (A,B) and at E11.5 (C,D). (E–H) Generation of mATH1+ progenitors adjacent to the roof plate. At E10.5 (E,H), mATH1+ cell number is normal in Gdf7 mutants. By E11.5 (F,H), the number of mATH1+ cells in Gdf7 mutant embryos is significantly reduced (to ∼40%), and at E12.5 (G,H), Gdf7 mutants have only 10% as many mATH1+ cells as wild-type siblings. The depletion of mATH1+ cells in the cervical spinal cord was detected in all E12.5 Gdf7 homozygous mutants examined (n = 8–20 sections from 18 embryos). (H) Quantitative analysis of the mATH1+ progenitor population in wild-type and homozygous mutant embryos (mean ± s.d., n = 10–25 sections from two to six embryos of each genotype). In addition, we detected no difference in the number of mATH1+ progenitors in Gdf7m1/+ heterozygotes as compared with wild-type siblings. (I–K) In situ hybridization showing the location of mATH1+ and Ngn1+ cells in wild-type and Gdf7m1 mutant embryos at E12.5. In wild-type embryos, mATH1+ progenitors (I, top) are interposed between Ngn1+ progenitors (J) and Msx1+ roof plate cells (summarized in M). Thus, the mATH1 progenitor domain appears as a region of unlabeled cells (between broken lines) in the wild-type spinal cord hybridized with Ngn1 and Msx1 probes (K, top). In Gdf7m1 mutant embryos, the loss of mATH1+ cells (I, bottom) is accompanied by a dorsal shift in the position of Ngn1+ progenitors (J), and the unlabeled region between Ngn1+ neural cells and Msx1+ roof plate cells is eliminated (K, top, summarized in N). The distance between the domains of Ngn1 progenitors (indicated by broken lines in J) is 89 ± 14 μm in wild-type and 43 ± 5 μm in Gdf7m1 homozygote embryos (mean ± s.d.; n = 10 sections from four embryos of each genotype). There is no difference in the mean width of the Msx1+ roof plate in wild-type and mutant embryos (see A). (L) Detection of apoptotic cell death by end labeling of fragmented DNA (TUNEL assay) in the dorsal spinal cord in E12.5 wild-type and Gdf7m1 mutant embryos. Very few dying cells are detected in or near the mATH progenitor domain in wild-type embryos or in mutant littermates that lack late mATH1+ cells. In contrast, abundant cell death was detected in other tissues, for example, in the tail bud and in the distal limb, in both wild-type and mutant embryos (data not shown). (M,N) Summary showing positions of neural progenitors in the dorsal spinal cord in wild-type and Gdf7m1 mutant embryos at E12.5.
