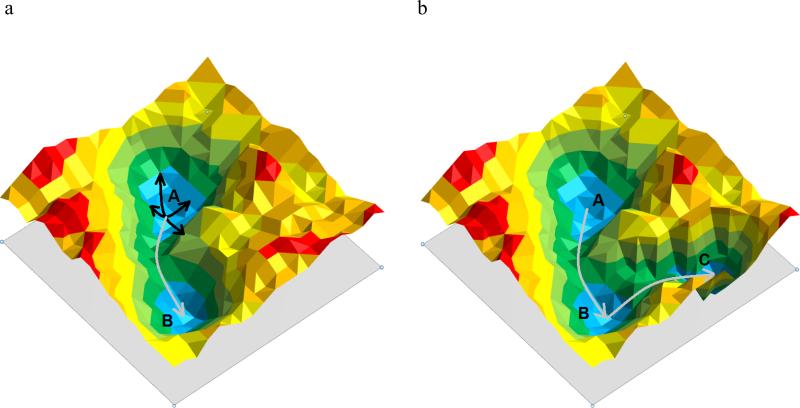
Figure 5.
(a) 2D model of a free-energy landscape of a protein system with the apo structure represented by energy minimum A and the holo structure by energy minimum B. Based on the encoding hypothesis, protein motion can be reduced to collective variables (black arrows). A linear combination of these collective variables allows the transition over low energy barriers (gray arrow) to the holo structure of the protein. (b) If holo structure (C) and apo structure (A) are separated by another stable conformation (B) the apo structure may only encode the transition to state B and ligand binding may be necessary to stabilize state B and induce a conformational change to the holo structure C.