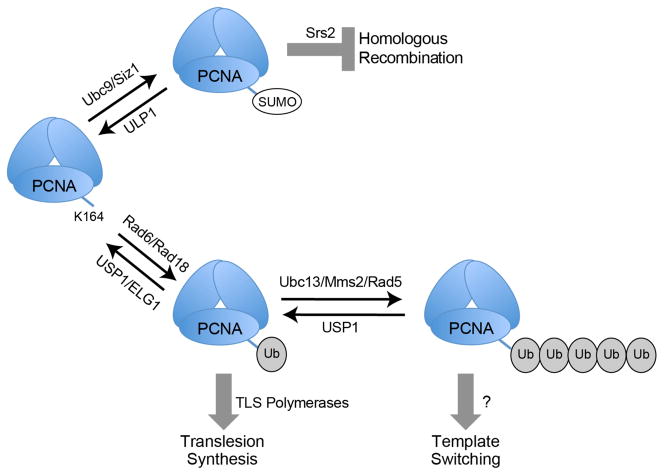
Figure 1.
PCNA modifications occur following DNA replication stress. In response to DNA damage stalling the DNA replication fork, K164 of PCNA can either be SUMOylated (SUMO) by Ubc9/Siz1 or monoubiquitylated (Ub) by Rad6/Rad18. The former modification inhibits inappropriate homologous recombination by recruiting the helicase Srs2, and the latter attracts specialized polymerases that carry out translesion synthesis. K164 monoubiquitylation can also be further extended by Ubc13/Mms2/Rad5 to initiate template switching by a currently unknown mechanism. PCNA SUMOylation and ubiquitylation are both reversible – SUMO is removed by ULP1 and ubiquitin is removed by USP1/ELG1.