Figure 1.
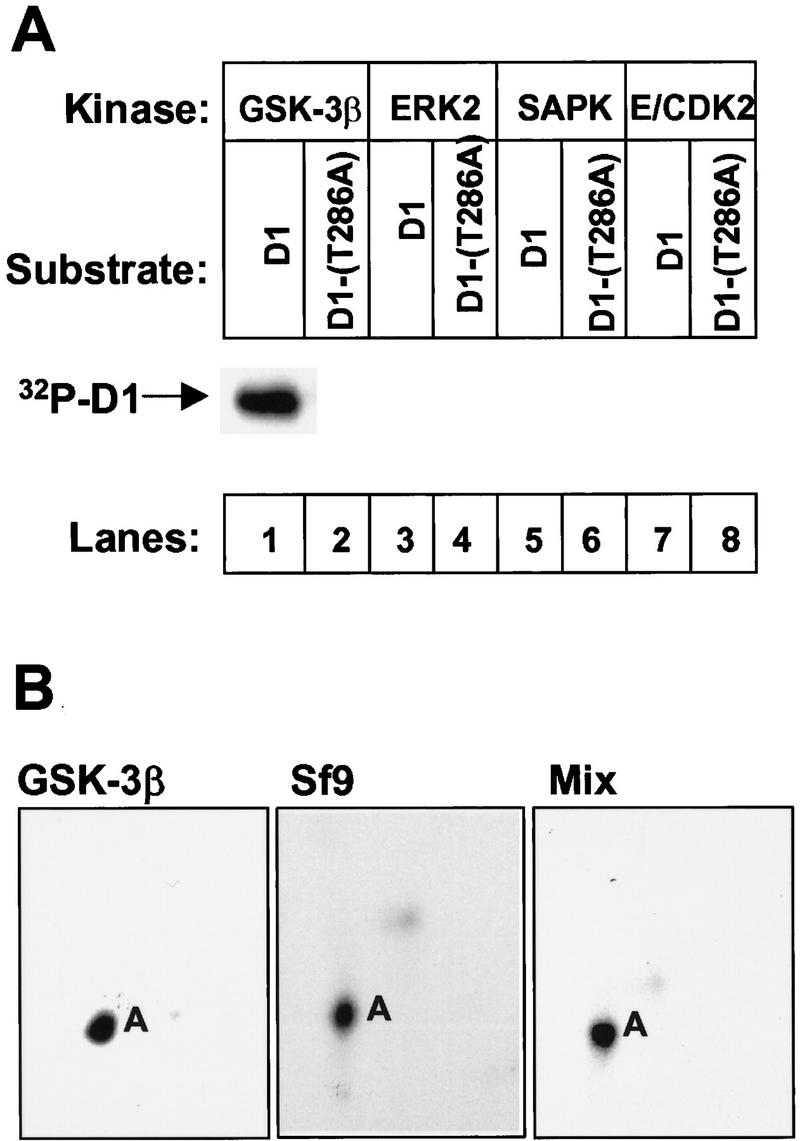
GSK-3β phosphorylates cyclin D1 on Thr-286. (A) Cyclin D1 (odd lanes) or cyclin D1-(T286A) (even lanes) immunoprecipitated from Sf9 cells infected with baculoviruses encoding D1 and CDK4 were mixed with recombinant GSK-3β (lanes 1,2), ERK2 (lanes 3,4), SAPK (lanes 5,6), or cyclin E–CDK2 (lanes 7,8) plus [γ-32P]ATP. After incubation at 30°C for 30 min, phosphorylated proteins were separated on a denaturing polyacrylamide gel, transferred to an Immobilon-P membrane, and visualized by autoradiography. The position of phosphorylated cyclin D1 is indicated. (B) Membrane slices containing cyclin D1 phosphorylated by GSK-3β in vitro (left), phosphorylated by endogenous Sf9 kinases (middle), or by a mixture of the two (right) were digested with trypsin and separated sequentially by electrophoresis and ascending chromatography. Phosphopeptides were visualized by autoradiographic exposure for 48 hr. The phosphopeptide containing Thr-286 was previously designated peptide A. Serine-containing peptides phosphorylated at lower stoichiometry can only be visualized after longer exposures (Kato et al. 1994; Diehl et al. 1997).
