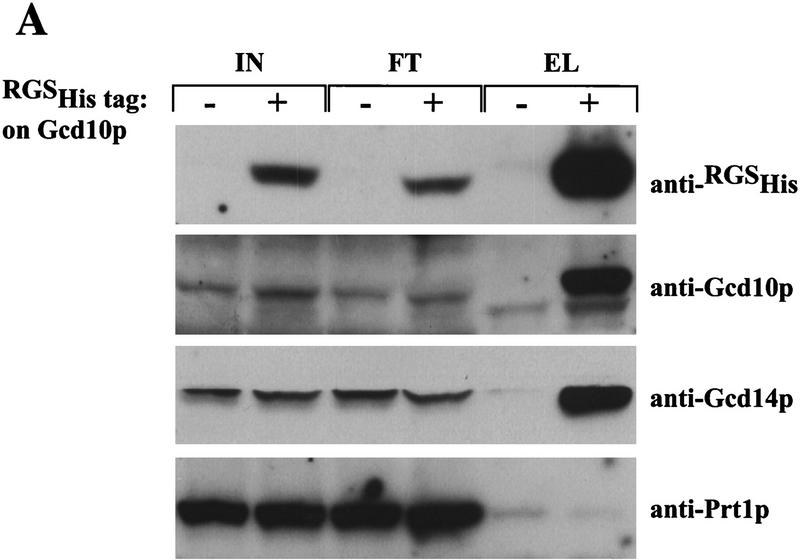
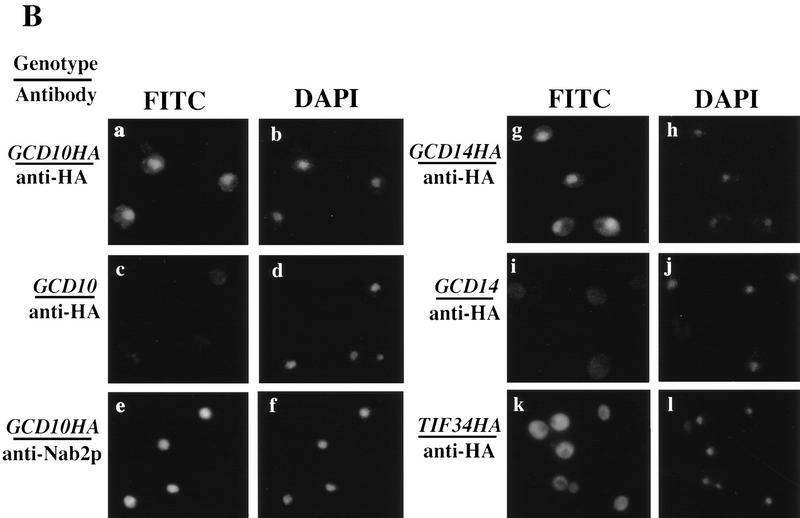
Figure 5.
Gcd10p and Gcd14p form a stable nuclear complex in vivo. (A) Whole cell extracts were prepared from isogenic strains LPY251 (GCD10) and LPY252 (GCD10–His) containing wild-type and His-tagged Gcd10p, respectively, as described (Phan et al. 1998). Each clarified extract was batch-bound to 50 μl of Ni2+–agarose (Qiagen) in H2O (50% vol/vol) for 1 hr at 4°C. Proteins bound to Ni2+–agarose were collected by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 2 min, washed four times with 300 μl of breaking buffer, and batch-eluted with 50 μl of breaking buffer containing 250 mm imidazole. Aliquots containing 10% of the input cell extracts (IN), 10% of the flowthrough wash (FT), and 100% of the eluate (EL) were resolved by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblot analysis using monoclonal anti-RGSHis antibodies (1:500; Qiagen) directed against the tag on His–Gcd10p, and with polyclonal antibodies directed against Gcd10p (1:500), Gcd14p (1:500), or Prt1p(1:1000). (B) Indirect immunofluorescence was used to study the subcellular distribution of HA epitope-tagged forms of Gcd10p, Gcd14p, and Tif34p in strains YJA142 (GCD10–HA; a,b), YJA143 (GCD10; c,d), Hm296 bearing pRC64 (GCD14–HA; g,h), Hm296 bearing pRC62 (GCD14; i,j), and KAY8 (TIF34–HA; k,l), as described previously (Anderson et al. 1993). All antibodies were diluted in PBS, 5% non-fat dried milk. The affinity-purified 12CA5 monoclonal antibody against the HA epitope (at 20 μg/ml; Boehringer Mannheim) was used to probe strains expressing HA-tagged proteins and the isogenic control strains lacking tagged proteins (a,c,g,i,k). Monoclonal antibody 1E4 (at 1:750 dilution; Wilson et al. 1994) was used to detect Nab1p in strain YJA142 (e). Detection of the primary antibodies was accomplished using a fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated secondary antibody (a,c,e,g,i,k) and the DNA distribution was visualized by DAPI (b,d,f,h,j,l).