Fig. 8.
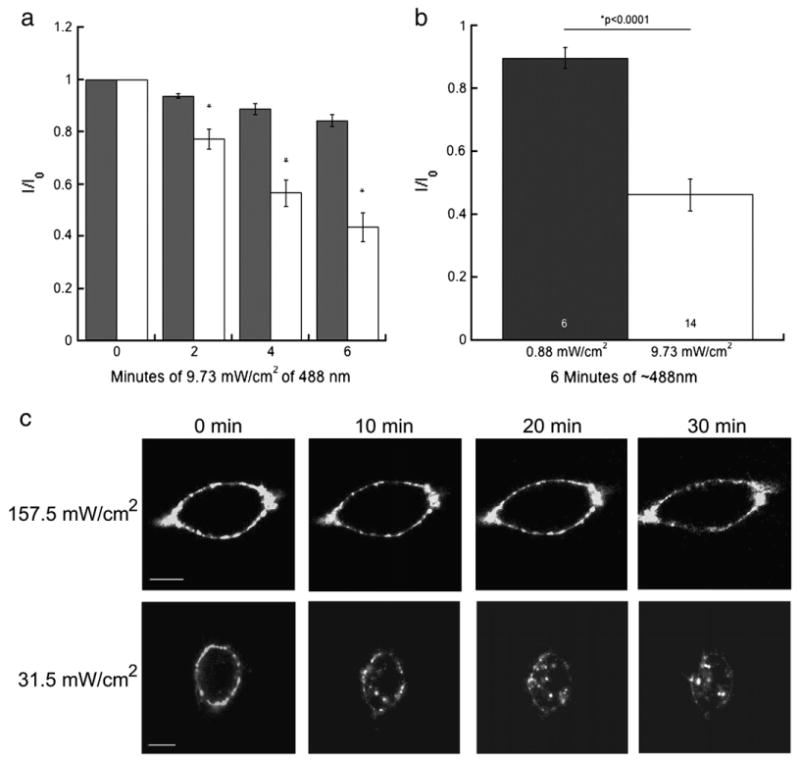
Fluorescence inactivation of 5-HT3A/BBS receptor function and internalization is dependent upon light intensity and duration of exposure. HEK-293 cells stably expressing 5-HT3A/BBS receptors were incubated in the presence or absence of BTX/488. Currents were elicited with 30 μM 5-HT every minute and exposed to 9.73 mW/cm2 of ∼488 nm light from a 100 W mercury arc lamp for 6 min. a) Peak amplitudes expressed as a proportion of the initial current (I0). The * indicates currents of BTX/488 labeled 5-HT3A/BBS receptors that were significantly (p<0.0001) different from currents elicited by cells exposed to light only (n = 14). Two-way ANOVA analysis indicated a significant (p<0.0001) interaction between the duration of light exposure and the presence of the BTX/488. b) The average peak amplitude of BTX/488 labeled 5-HT3A/BBS after 6 min of either 9.73 mW/cm2 or 0.88 mW/cm2 of ∼488 nm light. c) HEK-293 cells stably expressing 5-HT3A/BBS receptors with surface receptors labeled with BTX/488 were imaged every minute with either 157.5 mW/cm2 (top row) or 31.5 mW/cm2 (bottom row) of ∼488 nm light from an argon laser. c) Images of a representative cell at 0, 10, 20, and 30 min. Scale bar=10 μm.
