Figure 4. Rapid antidepressant-like behaviour mediated by decreased p-eEF2 and increased BDNF translation.
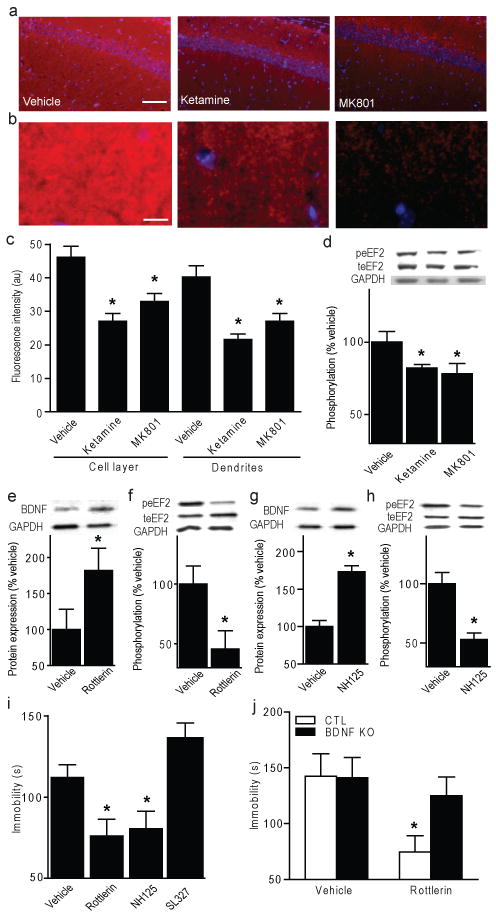
a, Images of CA1 pyramidal and stratum radiatum layers after acute vehicle, ketamine, or MK-801; scale bar=100 μm (red: peEF2, blue: DAPI). b, Stratum radiatum magnification; scale bar=20 μm. c, ImageJ analysis of average fluorescence intensity. ANOVA cell layer F2,23=13.13, P=0.0002 for treatment, dendrites F2,23=14.06, P=0.0001 for treatment (n=4/group). d, Densitometric analysis of peEF2 (normalized-total eEF2) in hippocampus after NMDAR antagonist. ANOVA F2,23=3.183, P=0.03 for treatment (n=8/group). e-h, Densitometric analysis. e, g, Significant increases in hippocampal BDNF protein (normalized-GAPDH) with rottlerin (5.0 mg/kg) versus vehicle (t-test *P<0.05), and NH125 (5.0 mg/kg) versus vehicle (*P<0.05). f, h, Significant decreases in peEF2 (normalized-total eEF2) versus vehicle (*P<0.05) and NH125 versus vehicle (t-test *P<0.05). i, Immobility in FST of WTs given acute rottlerin (5.0 mg/kg) or NH125 (5.0 mg/kg). ANOVA F3, 44= 8.13, P=0.0002 for treatment, Bonferroni post-hoc analysis shows significance with rottlerin or NH125 versus vehicle (*P<0.05), but not ERK inhibitor SL327 (10mg/kg). j, Immobility of BDNF KO or littermate CTLs given acute rottlerin (5.0 mg/kg), tested 30-minutes later in FST. ANOVA F1, 19=5.77, P=0.0267 for treatment, Bonferroni post-hoc analysis for rottlerin versus vehicle CTLs (*P<0.05) (n=5-7/group).
