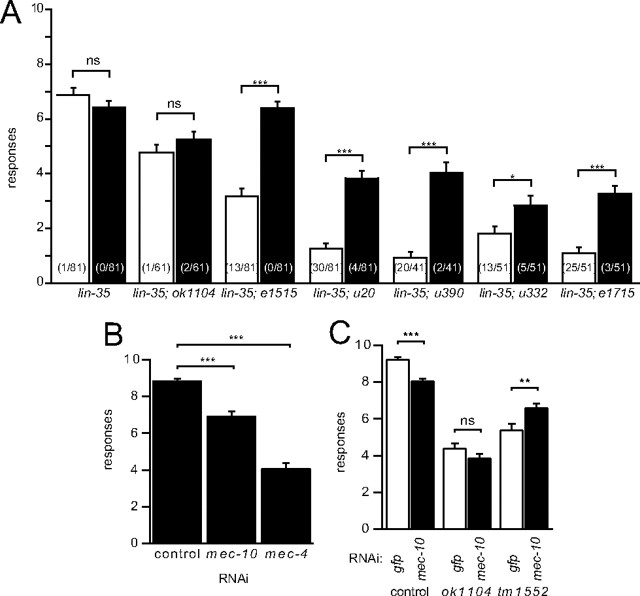
Figure 2.
Effects of mec-10 RNAi. A, RNAi against mec-10 in lin-35(n745) has no effect on animals with wild-type mec-10 or animals with the ok1104 deletion allele and enhances the touch sensitivity of animals with missense mutations in mec-10. Animals were fed bacteria expressing dsRNA against either GFP (white bars) or mec-10 (black bars) and assayed for touch response as described in Materials and Methods. Bars are mean ± SEM for n = 41–81 animals. Significance in all panels from Student's t test: ns, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.0001. Numbers in parentheses represent the number of animals that were completely unresponsive. B, RNAi against mec-10 results in a partial loss of touch sensitivity in a strain that is hypersensitive to RNAi [Punc-119sid-1 Punc-119gfp Pmec-6mec-6; lin-15b(n744)], whereas RNAi against mec-4 produces a more dramatic loss of touch sensitivity. Animals were fed bacteria expressing dsRNA against either GFP (control), mec-10, or mec-4 as indicated and assayed for touch response as described in Materials and Methods (mean ± SEM, n = 60 for each). C, RNAi against mec-10 in a hypersensitive RNAi background (Punc-119sid-1 Punc-119gfp Pmec-6mec-6) reduces the touch sensitivity of animals with wild-type mec-10 (control) and does not affect the touch response of animals with a deletion in mec-10 (ok1104 or tm1552). Animals were fed bacteria expressing dsRNA against either GFP (white bars) or mec-10 (black bars) and assayed for touch response as described in Materials and Methods (mean ± SEM, n = 90–100 for each).