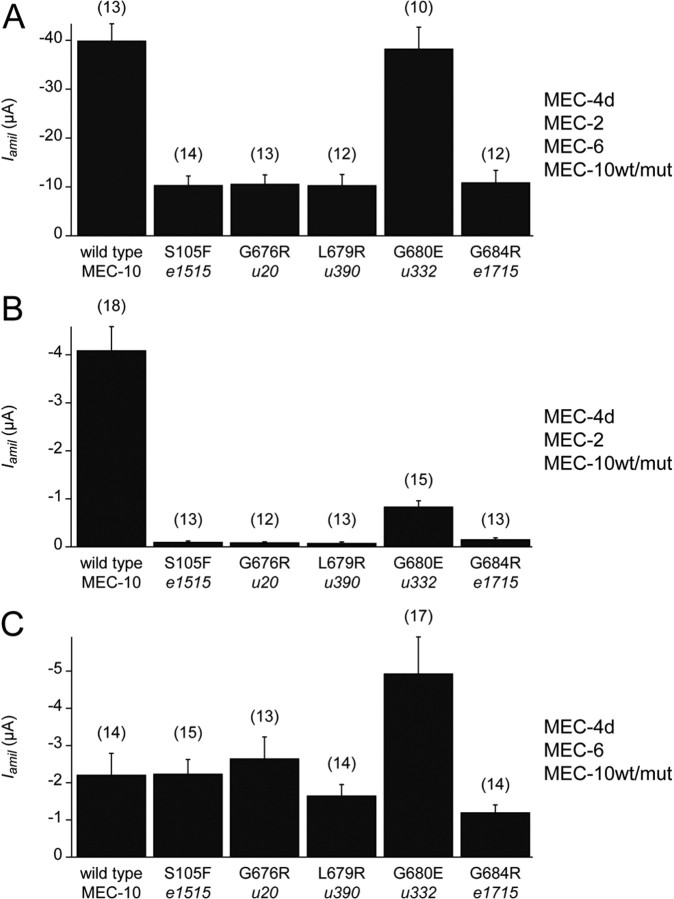
Figure 5.
MEC-10 mutant proteins inhibit the amiloride-sensitive current in Xenopus oocytes in a MEC-2-dependent manner. Amiloride-sensitive current (Iamil) recorded at −85 mV from the MEC-4d channel complex expressed with wild-type and mutant forms of MEC-10 as indicated beneath each bar (mean ± SEM, numbers in parentheses represent number of cells tested). A, Oocytes expressing MEC-4d, MEC-2, MEC-6, and wild-type and mutant forms of MEC-10 as noted. Except for the G680E variant, currents recorded from channels with MEC-10 variants were significantly different from currents from channels with wild-type MEC-10 (p < 0.00001, Student's t test). B, Oocytes expressing MEC-4d, MEC-2, and wild-type and mutant forms of MEC-10 as noted. Currents recorded from channels with MEC-10 variant proteins were significantly different from those from channels with wild-type MEC-10 (p < 0.00001, Student's t test). C, Oocytes expressing MEC-4d, MEC-6, and wild-type and mutant forms of MEC-10 as noted. Currents recorded from channels with G680E were significantly larger than currents from channels with wild-type MEC-10 (p < 0.05, Student's t test). No significant difference in current between channels with any of the other MEC-10 variants and those with wild-type MEC-10 (p = 0.12–0.97, Student's t test).