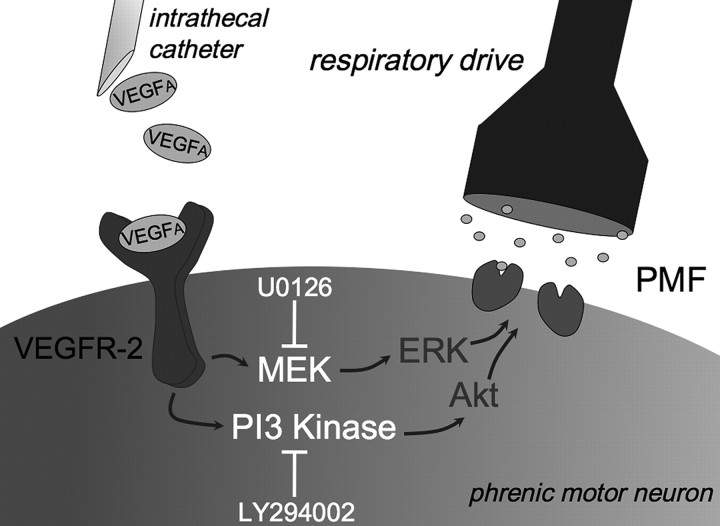
Figure 7.
Working model of VEGF-induced pMF. VEGF binds its most common receptor, VEGFR-2, a receptor tyrosine kinase. Downstream signaling includes both MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways. These cascades are required for full expression of VEGF-induced pMF because PI3K (LY294002) inhibitors abolish pMF, whereas the MEK inhibitor (U0126) attenuates VEGF-induced pMF. Mechanisms downstream from Akt and ERK are unknown. However, pMF may result from increased glutamate receptor insertion on the postsynaptic membrane between premotor and phrenic motor neurons. pMF may also arise from the ability of phosphorylated ERK to alter membrane excitability, such as changes in sodium channel gating properties that increase the likelihood of phrenic motor neuron firing (Stamboulian et al., 2010).