Figure 6.
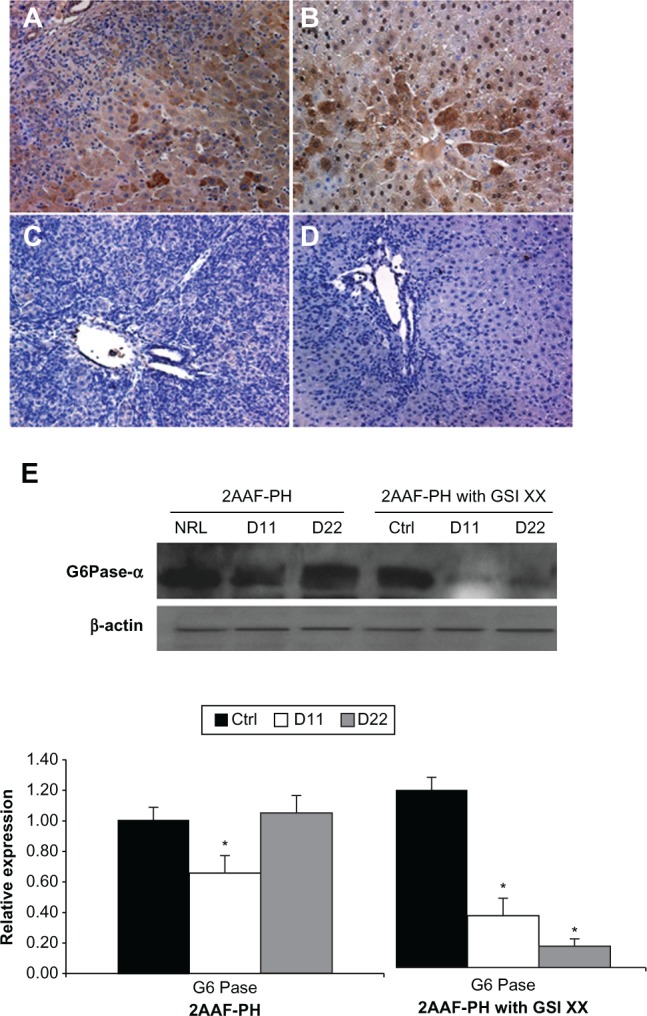
Lack of Notch expression leads to generation of functionally impaired hepatocytes. A–D) Immunohistochemical analysis of CYP3A2 expression at days 11 and 22 post-PH in both treatment groups, 2AAF-PH alone (A and B), as well as in combination with GSI XX treatment (C and D). In the 2AAF-PH group, there is a small amount of CYP3A2 expression at day 11 post-PH (A), which has significantly increased by day 22 post-PH (B), because the regeneration process has generally been completed by this point. In the GSI XX-treated group absolutely no CYP3A2 staining is seen at day 11 post-PH (C), and the levels increase only minimally by day 22 post-PH when Notch signaling is inhibited (D). A–D 200×. E) Top: Western analysis performed on protein isolated from liver taken at day 11 and day 22 post-PH from both treatment groups and probed with an antibody specific for the enzyme G6Pase-α. During 2AAF-PH alone, expression of G6Pase-α increases at day 11 post-PH and is even further elevated by day 22 post-PH, indicative of the formation of mature and functional hepatocytes. However, in the GSI XX-treated group, there is not as significant an increase in G6Pase-α levels at day 11, a difference that is even more pronounced in the day 22 post-PH sample. Bottom: semiquantitative analysis of G6Pase-α protein in both treatment groups for control, day 11 post-PH, and day 22 post-PH samples. Expression was normalized to β-actin and significance calculated compared with control animals.
Notes: *P < 0.01.
Abbreviations: GSI XX, γ-secretase inhibitor; PH, partial hepatectomy; 2AAF-PH, 2-acetylaminofluorine implantation followed by 70% surgical resection of the liver; G6Pase-α, glucose-6-phosphatase-α.
